| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
硫酸
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
丙酮
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
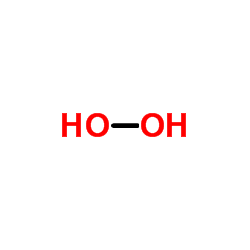 |
过氧化氢
CAS:7722-84-1 |
|
 |
D-葡萄糖-6,6-d2
CAS:18991-62-3 |
|
 |
D(+)-无水葡萄糖
CAS:50-99-7 |