| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
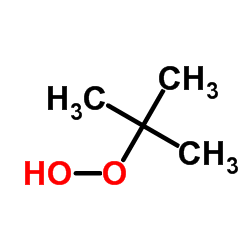 |
叔丁基过氧化氢
CAS:75-91-2 |
|
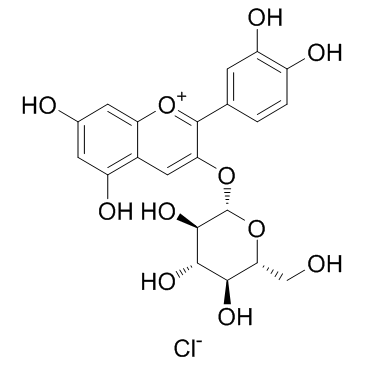 |
氯化失车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷
CAS:7084-24-4 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
叔丁基过氧化氢
CAS:75-91-2 |
|
 |
氯化失车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷
CAS:7084-24-4 |