Nourseothricin sulfate
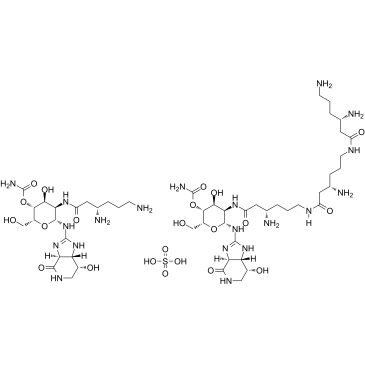
Nourseothricin sulfate structure
|
Common Name | Nourseothricin sulfate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 96736-11-7 | Molecular Weight | 502.522 | |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C50H94N20O22S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Nourseothricin sulfateNourseothricin sulfate (Streptothricin sulfate) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that destroys the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and is a dominant selective marker for Fonsecaea pedrosoi[1][2]. Nourseothricin sulfate inhibits protein biosynthesis in prokaryotic cells and strongly inhibits the growth of eukaryotes like fungi and can also be used as a elective marker for a wide range of organisms including bacteria, yeast, filamentous fungi, and plant cells[3]. |
| Name | (5ξ)-4-O-Carbamoyl-2-deoxy-2-{[(3S)-3,6-diaminohexanoyl]amino}-N- [(3aS,7R,7aS)-7-hydroxy-4-oxooctahydro-2H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-2 -ylidene]-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosylamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Nourseothricin sulfate (Streptothricin sulfate) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that destroys the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and is a dominant selective marker for Fonsecaea pedrosoi[1][2]. Nourseothricin sulfate inhibits protein biosynthesis in prokaryotic cells and strongly inhibits the growth of eukaryotes like fungi and can also be used as a elective marker for a wide range of organisms including bacteria, yeast, filamentous fungi, and plant cells[3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Escherichia coli resistance to neurosporin can be sensitive to resistant strains by eliminating their outer membrane resistance. The polycationic antibiotic, Nourseothricin, represents a mixture of several Streptothricins, mainly D and F. Obviously, although very slowly, it can pass the outer membrane via the porin pores. It has been shown earlier that Nourseothricin is able to generate some kind of channels into the outer membrane through which it can pass the cell wall. On the other hand, there are indications that resistant strains containing a Nourseothricin-inactivating acetyl transferase possess an additional protecting system, namely a reduced penetrability of the outer membrane[1]. |
| In Vivo | Nourseothricin is preferentially excreted via kidney and signs of nephrotoxicity can be observed after its administration. Renal handling of Nourseothricin is characterized in experiments on renal cortical slices under various experimental conditions. Following administration in vivo the renal tubular transport system for organic anions (p-aminohippurate, PAH) is not influenced by Nourseothricin. There is a high degree of accumulation of Nourseothricin in renal cortical slices. In contrast to PAH accumulation there is no influence of nitrogen atmosphere, simultaneous administration of PAH, probenecid or trishydroxyaminomethane on Nourseothricin accumulation. Age dependent differences in Nourseothricin accumulation does not exist[4]. |
| References |
[4]. Bräunlich H, et al. Renal handling of nourseothricin. Pharmazie. 1988 Mar;43(3):200-2. |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C50H94N20O22S |
| Molecular Weight | 502.522 |
| Exact Mass | 502.249969 |
| PSA | 276.87000 |
| LogP | -5.12 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.790 |
| Storage condition | -20C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | RD4240000 |
|
Extending the Schizosaccharomyces pombe molecular genetic toolbox.
PLoS ONE 9(5) , e97683, (2014) Targeted alteration of the genome lies at the heart of the exploitation of S. pombe as a model system. The rate of analysis is often determined by the efficiency with which a target locus can be manip... |
| 4-O-Carbamoyl-2-deoxy-2-{[(3S)-3,6-diaminohexanoyl]amino}-N-[(7R)-7-hydroxy-4-oxooctahydro-2H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-2-ylidene]-α-L-glycero-hexopyranosylamine |
| MFCD00165013 |
| α-L-glycero-Hexopyranosylamine, 2-deoxy-2-[[(3S)-3,6-diamino-1-oxohexyl]amino]-N-[(7R)-octahydro-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-2H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-2-ylidene]-, 4-carbamate |

