Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC
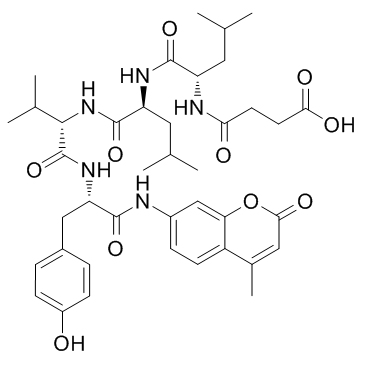
Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC structure
|
Common Name | Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 94367-21-2 | Molecular Weight | 763.87600 | |
| Density | 1.249g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1116.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C40H53N5O10 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 629.2ºC | |
Use of Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMCSuc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC is a fluorogenic substrate. Sequence: Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr. |
| Name | succinyl-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-7-amino-4-methylcoumarin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC is a fluorogenic substrate. Sequence: Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC (Suc-LLVY) is a membrane-permeable calpain-specific fluorogenic substrate, pteolytic hydrolysis of the peptidyl-7-amino bond liberates the highly fluorescent 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (AMC) moiety[1]. The effectof TGF-β on hydrolysis of these substrates (e.g Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC) are assessed. Biliary epithelial H69 cells are incubated with 10, 1, 0.1, or 0 ng/mL TGF-β for 24 h. Substrate hydrolysis is then fluorometrically assessed in cytosolic extracts. Basal activity is 1.12, 8.33, and 14.52 nmol AMC/mg protein/min for suc-LLVY-AMC, z-LLE-AMC, and z-LLL-AMC hydrolysis, respectively[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | Immunoprecipitation is carried out for the two sets of samples, using the same amount of protein. The 20 S and 26 S proteasome immunoprecipitates are washed with 50 mM Hepes/KOH (pH 7.5), and 50 mM Hepes/KOH (pH 7.5) containing 2 mMATP, respectively, prior to the determination of peptidase activity using 50 μM suc-Leu- Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC as substrate in these buffers[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.249g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1116.8ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C40H53N5O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 763.87600 |
| Flash Point | 629.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 763.37900 |
| PSA | 233.24000 |
| LogP | 5.17700 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.577 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Human high temperature requirement serine protease A1 (HTRA1) degrades tau protein aggregates.
J. Biol. Chem. 287(25) , 20931-41, (2012) Protective proteases are key elements of protein quality control pathways that are up-regulated, for example, under various protein folding stresses. These proteases are employed to prevent the accumu... |
|
|
Turnover of oxidatively damaged nuclear proteins in BV-2 microglial cells is linked to their activation state by poly-ADP-ribose polymerase.
FASEB J. 15(8) , 1460-2, (2001)
|
|
|
Activation of the cell death program by nitric oxide involves inhibition of the proteasome.
J. Biol. Chem. 274(28) , 19581-6, (1999) The ubiquitin/proteasome pathway mediates the degradation of many short-lived proteins that are critically involved in the regulation of cell proliferation and cell death, including the tumor suppress... |
| z-llvy-amc |
| suc-leu-leu-val-tyr-amc |
| suc-llvy-amc |
| suc-leu-leu-val-tyr-7-amino-4-methylcoumarin |
| chymotrypsin substrate iii,fluorogenic |
| n-succinyl-leu-leu-val-tyr 7-amido-4-methylcoumarin |
| MFCD00080248 |
| suc-leu-leu-val-tyr-mca |