2-Naphthoic acid
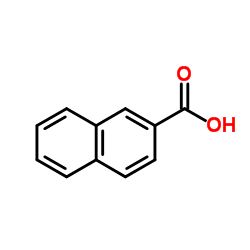
2-Naphthoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 2-Naphthoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 93-09-4 | Molecular Weight | 172.180 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 332.9±11.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H8O2 | Melting Point | 185-187 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 151.3±13.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 2-Naphthoic acid2-Naphthoic acid is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
| Name | 2-Naphthoic Acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2-Naphthoic acid is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 332.9±11.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 185-187 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C11H8O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 172.180 |
| Flash Point | 151.3±13.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 172.052429 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 3.13 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.673 |
| Water Solubility | <0.5 g/L (20 C) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | QL1050000 |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916399090 other aromatic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Regioselective oxidation of indole- and quinolinecarboxylic acids by cytochrome P450 CYP199A2.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85(6) , 1861-8, (2010) CYP199A2, a bacterial P450 monooxygenase from Rhodopseudomonas palustris, was previously reported to oxidize 2-naphthoic acid and 4-ethylbenzoic acid. In this study, we examined the substrate specific... |
|
|
A new analytical method to determine non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in surface water using in situ derivatization combined with ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
Talanta 129 , 552-9, (2014) Because of the high stability and potential toxic effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), it is important to closely monitor their concentrations in the environment using a sensitiv... |
|
|
Beta-cyclodextrin decorated nanostructured SERS substrates facilitate selective detection of endocrine disruptor chemicals.
Biosens. Bioelectron. 42 , 632-9, (2013) We demonstrate the selective detection of endocrine disruptor chemicals (EDCs) from river water using surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). By means of nanosphere lithography, the SERS substrate w... |
| 2-Naphthoic acid |
| isonaphthoic acid |
| β-Naphthoic acid |
| 2-Naphthalenecarboxylic acid |
| naphthalene-2-carboxylic acid |
| EINECS 202-217-8 |
| MFCD00004101 |
| 2-napthoic acid |
 CAS#:1592-38-7
CAS#:1592-38-7 CAS#:43210-74-8
CAS#:43210-74-8 CAS#:91-57-6
CAS#:91-57-6 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9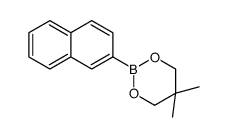 CAS#:627906-96-1
CAS#:627906-96-1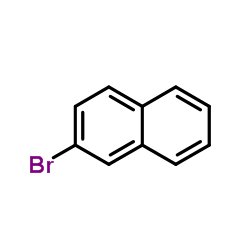 CAS#:580-13-2
CAS#:580-13-2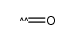 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2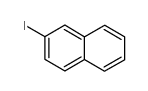 CAS#:612-55-5
CAS#:612-55-5 CAS#:13298-50-5
CAS#:13298-50-5 CAS#:39627-84-4
CAS#:39627-84-4 CAS#:14625-56-0
CAS#:14625-56-0 CAS#:141903-34-6
CAS#:141903-34-6 CAS#:939-26-4
CAS#:939-26-4 CAS#:92-70-6
CAS#:92-70-6 CAS#:21815-18-9
CAS#:21815-18-9![2-phenyl-1H-benzo[e]isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/304/130728-71-1.png) CAS#:130728-71-1
CAS#:130728-71-1 CAS#:20717-80-0
CAS#:20717-80-0
