Ascamycin
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 16:34:20
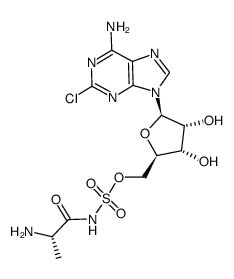
Ascamycin structure
|
Common Name | Ascamycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 91432-48-3 | Molecular Weight | 451.84300 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H18ClN7O7S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of AscamycinAscamycin is a 5'-O-sulfonamide ribonucleoside antibiotic produced by Streptomyces sp. JCM9888. Ascamycin has a selective antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas species with MIC values of 0.4 μg/mL, 12.5 μg/mL and 12.5 μg/mL for Xanthomonas citri, Xanthomonas oryzae and Mycobacterium phlei, respectively[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 2-chloro-5'-O-(N-(L-alanyl)sulfamoyl)adenosine (Ascamycin) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ascamycin is a 5'-O-sulfonamide ribonucleoside antibiotic produced by Streptomyces sp. JCM9888. Ascamycin has a selective antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas species with MIC values of 0.4 μg/mL, 12.5 μg/mL and 12.5 μg/mL for Xanthomonas citri, Xanthomonas oryzae and Mycobacterium phlei, respectively[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
MIC: 0.4 μg/mL (Xanthomonas citri), 12.5 μg/mL (Xanthomonas oryzae) and 12.5 μg/mL (Mycobacterium phlei)[1] |
| In Vitro | The Ascamycin has C2-chloroadenine as the base on C-1' which lacks the chlorine[1]. Ascamycin has a selective antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas species. When Ascamycin is dealanylated, Dealanylascamycin shows a broad antibacterial activity against various Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Xanthomonas citri is susceptible to Ascamycin by virtue of the Ascamycin-dealanylating enzyme on the cell surface[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C13H18ClN7O7S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 451.84300 |
| Exact Mass | 451.06800 |
| PSA | 226.18000 |
| LogP | 0.15910 |
| InChIKey | LZMCAAGVMFMSKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(N)C(=O)NS(=O)(=O)OCC1OC(n2cnc3c(N)nc(Cl)nc32)C(O)C1O |
| ascamycin |
| 2-chloro-5'-O-[N-(L-alanyl)sulfamoyl]adenosine (Ascamycin) |
| ((S)-2-Amino-propionyl)-sulfamic acid (2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-2-chloro-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxy-tetrahydro-furan-2-ylmethyl ester |