Chlorimuron-ethyl
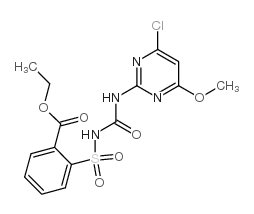
Chlorimuron-ethyl structure
|
Common Name | Chlorimuron-ethyl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 90982-32-4 | Molecular Weight | 414.82100 | |
| Density | 1.493 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H15ClN4O6S | Melting Point | 180-182°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Chlorimuron-ethylChlorimuron-ethyl induces oxidative stress. Chlorimuron-ethyl is an important herbicide that has been widely used in soybean production[1]. |
| Name | chlorimuron-ethyl |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Chlorimuron-ethyl induces oxidative stress. Chlorimuron-ethyl is an important herbicide that has been widely used in soybean production[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Chlorimuron-ethyl (30 mg/kg) treatment causes significant damage to CHL accumulation[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.493 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 180-182°C |
| Molecular Formula | C15H15ClN4O6S |
| Molecular Weight | 414.82100 |
| Exact Mass | 414.04000 |
| PSA | 144.96000 |
| LogP | 3.37040 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.598 |
| InChIKey | NSWAMPCUPHPTTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)c1ccccc1S(=O)(=O)NC(=O)Nc1nc(Cl)cc(OC)n1 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H332 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | 36 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | DG5095000 |
| HS Code | 2935009012 |
| HS Code | 2935009012 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2935009012 ethyl 2-(n-((4-chloro-6-methoxypyrimidin-2-yl)carbamoyl)sulfamoyl)benzoate。supervision conditions:s(import or export registration certificate for pesticides)。VAT:17.0%。tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tarrif:6.5%。general tariff:35.0% |
|
Response of multiple seeded cocklebur and other cocklebur types to herbicide treatment.
Pest Manag. Sci. 61(7) , 643-8, (2005) Multiple seeded cocklebur has been found in the last decade in Texas, and described as a biotype of Xanthium strumarium L with up to 25 seeds per bur instead of the usual two. The multiple seeded bur ... |
|
|
Magnetic solid-phase extraction of sulfonylurea herbicides in environmental water samples by Fe3O4@dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride@silica magnetic particles.
Anal. Chim. Acta 747 , 29-35, (2012) A magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) method coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was proposed for the determination of five sulfonylurea herbicides (bensulfuron-methyl, prosu... |
|
|
Elucidating the specificity of binding of sulfonylurea herbicides to acetohydroxyacid synthase.
Biochemistry 44(7) , 2330-8, (2005) Acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS, EC 2.2.1.6) is the target for the sulfonylurea herbicides, which act as potent inhibitors of the enzyme. Chlorsulfuron (marketed as Glean) and sulfometuron methyl (mar... |
| ethyl 2-[[[[(4-chloro-6-methoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]benzoate |
| Chlorimuron ethyl |
| MFCD00128063 |
| Chlorimuron-ethyl |
| ethyl 2-{[(4-chloro-6-methoxypyrimidin-2-yl)carbamoyl]sulfamoyl}benzoate |
| ethyl 2-(4-chloro-6-methoxypyrimidin-2-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)benzoate |

