2,6-Dichlorophenol
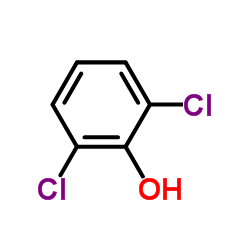
2,6-Dichlorophenol structure
|
Common Name | 2,6-Dichlorophenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 87-65-0 | Molecular Weight | 163.001 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 219.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Cl2O | Melting Point | 65 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 94.9±15.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | 2,6-dichlorophenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 219.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 65 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Cl2O |
| Molecular Weight | 163.001 |
| Flash Point | 94.9±15.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 161.963913 |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 2.61 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.1±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.594 |
| InChIKey | HOLHYSJJBXSLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Oc1c(Cl)cccc1Cl |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides. |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 20 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H314 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S27-S36/37/39-S37/39-S45-S36/37-S16 |
| RIDADR | UN 2020 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | SK8750000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2908199090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2908199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2908199090. derivatives of polyphenols or phenol-alcohols containing only halogen substituents and their salts. VAT:17.0%. tax rebate rate:9.0%. supervision conditions:None. MFN tariff:5.5%. general tariff:30.0% |
|
cIEF for rapid pKa determination of small molecules: a proof of concept.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 63 , 14-21, (2014) A capillary isoelectric focusing (cIEF) method was developed for the determination of the ionization constants (pKa) of small molecules. Two approaches used to decrease the electroosmotic flow (EOF) w... |
|
|
Calculating virtual log P in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and its derived parameters deltalog P(N)(oct-alk) and log D(pH)(alk).
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 3269-79, (2005) Growing interest in the use of both the logarithm of the partition coefficient of the neutral species in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and the difference between log P(N)(oct) (the logarithm... |
|
|
Physico-chemical properties, antioxidant activity and mineral contents of pineapple genotypes grown in china.
Molecules 19(6) , 8518-32, (2014) The fruit physico-chemical properties, antioxidant activity and mineral contents of 26 pineapple [Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.] genotypes grown in China were measured. The results showed great quantitati... |
| 2,6-Dichlor-phenol |
| EINECS 201-761-3 |
| 2,6-Dichlorfenol |
| 2,6-Dichlorophenol |
| 2,6-Cl2-C6H3OH |
| 2,4,6-trichlorophenole |
| 2,6-dichloro-phenol |
| Phenol, 2,6-dichloro- |
| HO-2,6-C6H3Cl2 |
| Phenol,2,6-dichloro |
| 2,6-Dichlorfenol [Czech] |
| RCRA waste no. U082 |
| MFCD00002176 |
| 2.6-Dichlor-1-hydroxy-benzol |
| RCRA waste number U082 |
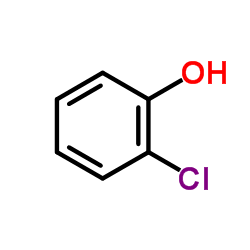 CAS#:95-57-8
CAS#:95-57-8 CAS#:3336-41-2
CAS#:3336-41-2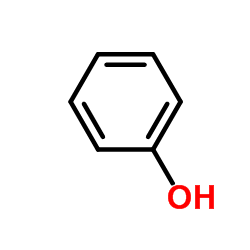 CAS#:108-95-2
CAS#:108-95-2 CAS#:188645-80-9
CAS#:188645-80-9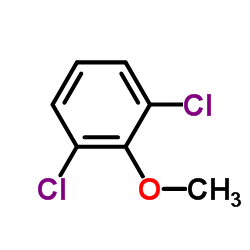 CAS#:1984-65-2
CAS#:1984-65-2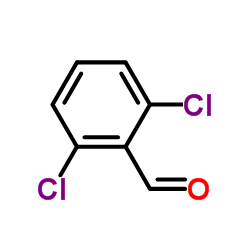 CAS#:83-38-5
CAS#:83-38-5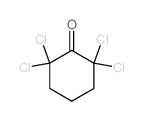 CAS#:3776-30-5
CAS#:3776-30-5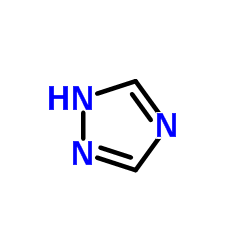 CAS#:288-88-0
CAS#:288-88-0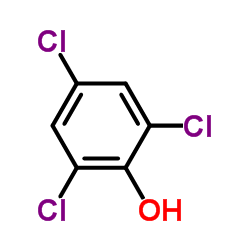 CAS#:88-06-2
CAS#:88-06-2 CAS#:3598-66-1
CAS#:3598-66-1 CAS#:3217-15-0
CAS#:3217-15-0 CAS#:19740-72-8
CAS#:19740-72-8 CAS#:98-95-3
CAS#:98-95-3 CAS#:147102-65-6
CAS#:147102-65-6 CAS#:1806-29-7
CAS#:1806-29-7 CAS#:1928-49-0
CAS#:1928-49-0
