Acenaphthoquinone

Acenaphthoquinone structure
|
Common Name | Acenaphthoquinone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 82-86-0 | Molecular Weight | 182.175 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 362.5±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H6O2 | Melting Point | 249-252 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 150.2±4.4 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | acenaphthoquinone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 362.5±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 249-252 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C12H6O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 182.175 |
| Flash Point | 150.2±4.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 182.036774 |
| PSA | 34.14000 |
| LogP | 2.28 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.746 |
| Water Solubility | INSOLUBLE |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN 2920 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AB1024500 |
| Packaging Group | II; III |
| Hazard Class | 4.1 |
| HS Code | 29146990 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2914399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2914399090. other aromatic ketones without other oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:5.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Addition of phenylacetylene to a magnesium complex of monoiminoacenaphtheneone (dpp-mian).
Dalton Trans. 44 , 20532-41, (2015) In the presence of formic acid, acenaphthenequinone (AQ) reacts with one molar equivalent of 2,6-diisopropylaniline in toluene to give monoiminoacenaphtheneone (3, dpp-mian) in good yield. Reduction o... |
|
|
Planarity and constraint of the carbonyl groups in 1,2-diones are determinants for selective inhibition of human carboxylesterase 1.
J. Med. Chem. 50 , 5727-34, (2007) Carboxylesterases (CE) are ubiquitous enzymes responsible for the detoxification of xenobiotics, including numerous clinically used drugs. Therefore, the selective inhibition of these proteins may pro... |
|
|
CaCl(2) as a bifunctional reusable catalyst: diversity-oriented synthesis of 4H-pyran library under ultrasonic irradiation.
Mol. Divers. 16(4) , 669-83, (2012) CaCl(2) is applied as an efficient reusable and eco-friendly bifunctional catalyst for the one-pot three-component synthesis of 4H-pyrans under ultrasonic irradiation. A broad range of substrates incl... |
| acenaphthenequinone |
| MFCD00003805 |
| Acenaphthoquinone |
| EINECS 201-441-3 |
| 1,2-Acenaphthylenedione |
| acenaphthylene-1,2-dione |
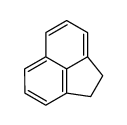 CAS#:83-32-9
CAS#:83-32-9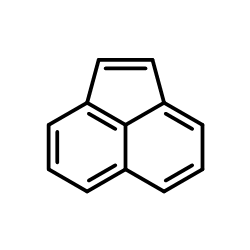 CAS#:208-96-8
CAS#:208-96-8 CAS#:14209-08-6
CAS#:14209-08-6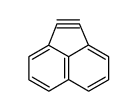 CAS#:13093-45-3
CAS#:13093-45-3![Ethyl 2-oxo-3'-phenylspiro[acenaphthylene-1-(2H),5'(4'H)-isoxazole]-4'-carboxylate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/334/103457-73-4.png) CAS#:103457-73-4
CAS#:103457-73-4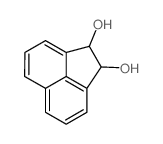 CAS#:2963-86-2
CAS#:2963-86-2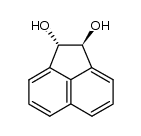 CAS#:2963-87-3
CAS#:2963-87-3 CAS#:2235-15-6
CAS#:2235-15-6 CAS#:5116-63-2
CAS#:5116-63-2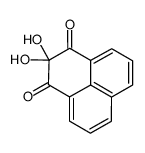 CAS#:18931-20-9
CAS#:18931-20-9 CAS#:14619-86-4
CAS#:14619-86-4 CAS#:17976-92-0
CAS#:17976-92-0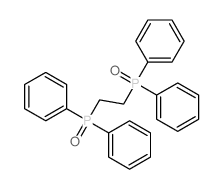 CAS#:4141-50-8
CAS#:4141-50-8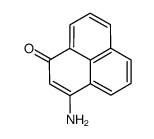 CAS#:23177-30-2
CAS#:23177-30-2 CAS#:20485-57-8
CAS#:20485-57-8 CAS#:19274-72-7
CAS#:19274-72-7![2-[2,6-di(propan-2-yl)phenyl]iminoacenaphthylen-1-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/177/187605-59-0.png) CAS#:187605-59-0
CAS#:187605-59-0 CAS#:1932-10-1
CAS#:1932-10-1![N-[[2-(phenylhydrazinylidene)acenaphthen-1-ylidene]amino]aniline structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/096/1932-06-5.png) CAS#:1932-06-5
CAS#:1932-06-5
