N-Isopropylaniline
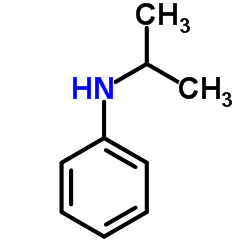
N-Isopropylaniline structure
|
Common Name | N-Isopropylaniline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 768-52-5 | Molecular Weight | 135.206 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 203.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H13N | Melting Point | -32°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 81.3±14.2 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | N-Isopropylaniline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 203.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -32°C |
| Molecular Formula | C9H13N |
| Molecular Weight | 135.206 |
| Flash Point | 81.3±14.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 135.104797 |
| PSA | 12.03000 |
| LogP | 2.47 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.3±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.546 |
| InChIKey | FRCFWPVMFJMNDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C)Nc1ccccc1 |
| Water Solubility | <0.01 g/100 mL at 21 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H330-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P284-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R23;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S45-S7/9 |
| RIDADR | 2810 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BY4190000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2921420090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2921420090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2921420090 aniline derivatives and their salts VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Characterization of two novel propachlor degradation pathways in two species of soil bacteria.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65(2) , 802-6, (1999) Propachlor (2-chloro-N-isopropylacetanilide) is an acetamide herbicide used in preemergence. In this study, we isolated and characterized a soil bacterium, Acinetobacter strain BEM2, that was able to ... |
|
|
Rapid mineralisation of the herbicide isoproturon in soil from a previously treated Danish agricultural field.
Pest Manag. Sci. 59(10) , 1118-24, (2003) Mineralisation of the phenylurea herbicide isoproturon (3-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea) and two of its known metabolites, 3-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1-methylurea (monodesmethyl-isoproturon) and 4-i... |
|
|
Propachlor and N-isopropylaniline residues in onions (Allium cepa) and muck soils.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 47(1) , 104-11, (1991)
|
| N-(1-Methylethyl)benzenamine |
| PHENYLISOPROPYLAMINE |
| N-Isopropylaniline |
| N-iso-Propylaniline |
| 2-(Phenylamino)propane |
| Benzenamine, N-(1-methylethyl)- |
| N-isopropyl-1-amino-benzene |
| EINECS 212-196-7 |
| N-(1-methylethyl)aniline |
| N-(Propan-2-yl)anilin |
| N-propan-2-ylaniline |
| N-(propan-2-yl)aniline |
| MFCD00026347 |
 CAS#:108-18-9
CAS#:108-18-9 CAS#:75-30-9
CAS#:75-30-9 CAS#:591-50-4
CAS#:591-50-4 CAS#:75-31-0
CAS#:75-31-0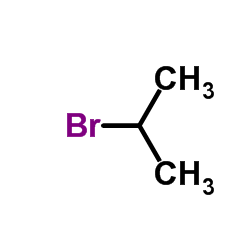 CAS#:75-26-3
CAS#:75-26-3 CAS#:67-64-1
CAS#:67-64-1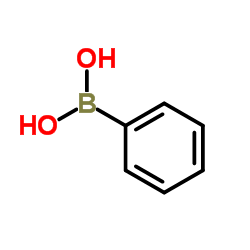 CAS#:98-80-6
CAS#:98-80-6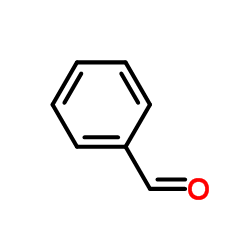 CAS#:100-52-7
CAS#:100-52-7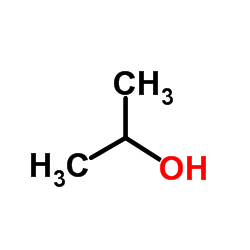 CAS#:67-63-0
CAS#:67-63-0 CAS#:10545-45-6
CAS#:10545-45-6 CAS#:108221-79-0
CAS#:108221-79-0 CAS#:4107-98-6
CAS#:4107-98-6 CAS#:98-95-3
CAS#:98-95-3 CAS#:93957-49-4
CAS#:93957-49-4 CAS#:948-65-2
CAS#:948-65-2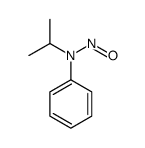 CAS#:24642-83-9
CAS#:24642-83-9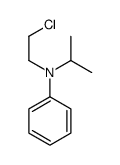 CAS#:25012-17-3
CAS#:25012-17-3
