α-D-Glucopyranuronic acid

α-D-Glucopyranuronic acid structure
|
Common Name | α-D-Glucopyranuronic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6556-12-3 | Molecular Weight | 194.139 | |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 495.2±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O7 | Melting Point | 159-161ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 211.1±22.2 °C | |
Use of α-D-Glucopyranuronic acidD-Glucuronic acid is an important intermediate isolated from many gums. D-Glucuronic acid and its derivative glucuronolactone are as a liver antidote in the prophylaxis of human health. D-Glucuronic acid has an anti-inflammatory effect for the skin[1]. |
| Name | aldehydo-D-glucuronic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | D-Glucuronic acid is an important intermediate isolated from many gums. D-Glucuronic acid and its derivative glucuronolactone are as a liver antidote in the prophylaxis of human health. D-Glucuronic acid has an anti-inflammatory effect for the skin[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 495.2±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 159-161ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 194.139 |
| Flash Point | 211.1±22.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 194.042648 |
| PSA | 135.29000 |
| LogP | -2.88 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.685 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator (+4°C) |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 37/39-26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | LZ8836600 |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918990090. other carboxylic acids with additional oxygen function and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Extraction optimization, characterization and antioxidant activity in vitro of polysaccharides from mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves.
Carbohydr. Polym. 128 , 52-62, (2015) Extraction optimization, characterization and antioxidant activity in vitro of polysaccharides from mulberry leaves (MLP) were investigated in the present study. The optimal extraction conditions with... |
|
|
Modulation of biomechanical properties of hyaluronic acid hydrogels by crosslinking agents.
J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 103 , 3072-80, (2015) Modulation of both mechanical properties and biocompatibilities of hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogels is very importance for their applications in biomaterials. Pure HA solution was converted into a hydro... |
|
|
GlxA is a new structural member of the radical copper oxidase family and is required for glycan deposition at hyphal tips and morphogenesis of Streptomyces lividans.
Biochem. J. 469 , 433-44, (2015) Streptomyces lividans displays a distinct dependence on copper to fully initiate morphological development. Evidence has accumulated to implicate the participation of an extracytoplasmic cuproenzyme i... |
| α-D-glucuronic acid |
| D-Glucuronic acid |
| EINECS 229-486-4 |
| D-Glucopyranuronic acid |
| MFCD00077778 |
| (2S,3S,4S,5R)-2,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxy-6-oxohexanoic acid |
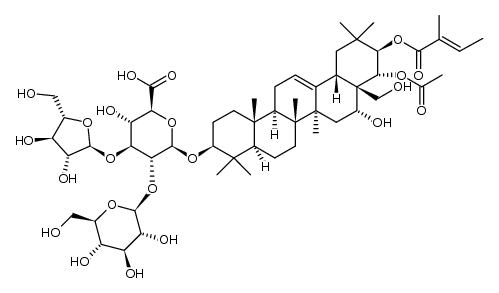 CAS#:1361004-77-4
CAS#:1361004-77-4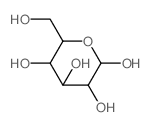 CAS#:2280-44-6
CAS#:2280-44-6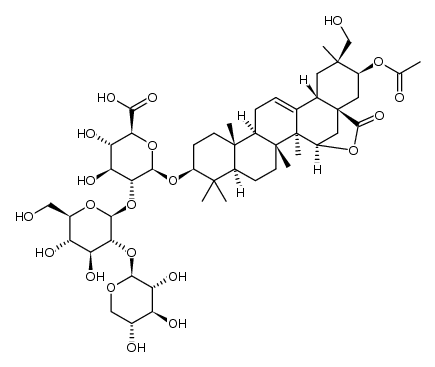 CAS#:1266208-13-2
CAS#:1266208-13-2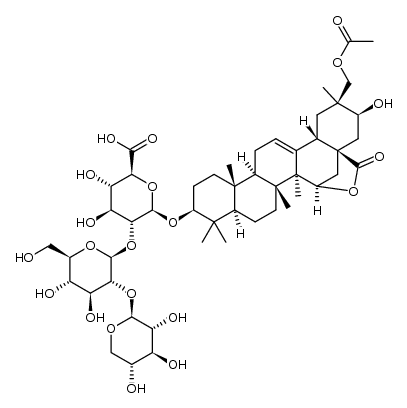 CAS#:1266208-15-4
CAS#:1266208-15-4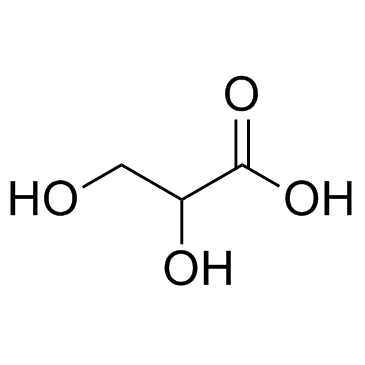 CAS#:473-81-4
CAS#:473-81-4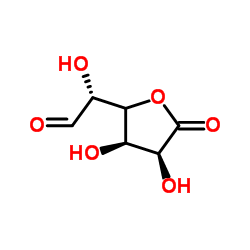 CAS#:32449-92-6
CAS#:32449-92-6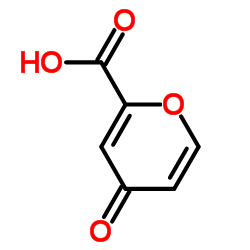 CAS#:499-05-8
CAS#:499-05-8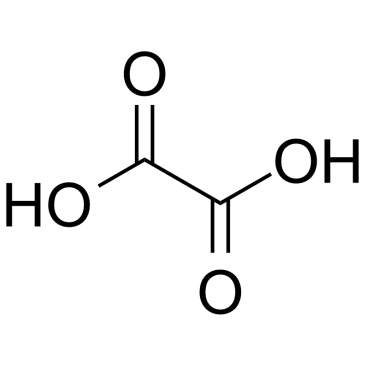 CAS#:144-62-7
CAS#:144-62-7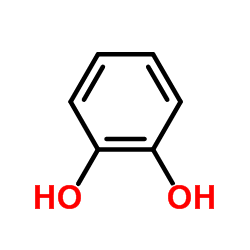 CAS#:120-80-9
CAS#:120-80-9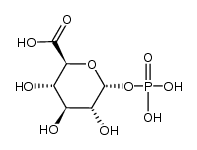 CAS#:10345-04-7
CAS#:10345-04-7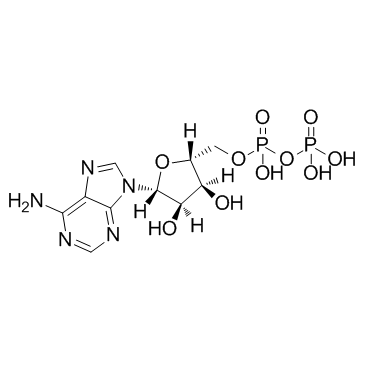 CAS#:58-64-0
CAS#:58-64-0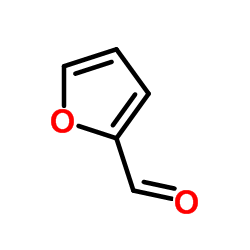 CAS#:98-01-1
CAS#:98-01-1
