2,4,6-Trichloroaniline
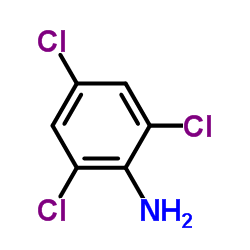
2,4,6-Trichloroaniline structure
|
Common Name | 2,4,6-Trichloroaniline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 634-93-5 | Molecular Weight | 196.462 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 258.4±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Cl3N | Melting Point | 75 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 110.1±25.9 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | 2,4,6-Trichloroaniline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 258.4±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 75 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Cl3N |
| Molecular Weight | 196.462 |
| Flash Point | 110.1±25.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 194.940933 |
| PSA | 26.02000 |
| LogP | 3.74 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.626 |
| Stability | Stable, but may be light or air sensitive. Incompatible with acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroformates, strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 21.5 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H311-H331-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P273-P280-P301 + P310-P311-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R23/24/25;R33;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S36/37-S45-S60-S61-S28A |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BZ0250000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2921420090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2921420090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2921420090 aniline derivatives and their salts VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
[Hygienic standardization of trichloroaniline in reservoir water].
Gig. Sanit. (3) , 83-4, (1985)
|
|
|
[Study on method of sampling and analysis of trichloroaniline in the air].
Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 27(2) , 87-9, (1998) Trichloroaniline in the air was collected with 50% ethanol and separated with a column OV-17:OV-210 ECD as a detector. The best conditions of sampling and determining were selected through the orthogo... |
|
|
The use of clays to sequestrate organic pollutants. Leaching experiments.
Chemosphere 73(11) , 1731-6, (2008) Leaching experiments are performed from clay-pollutant systems in order to evaluate the capability of clays to sequestrate organic pollutants from wastewaters. Reference kaolinite KGa-1b, montmorrillo... |
| 2,4,6-Trichlorophenylamine |
| 2,3-DIHYDROBENZO[1,4]DIOXINE-5-CARBONYL CHLORIDE 0.98 |
| Benzenamine, 2,4,6-trichloro- |
| 2,4,6-trichloro-aniline |
| 2,4,6-Trichloroaniline |
| 1-amino-2,4,6-trichlorobenzene |
| 2,4,6-Trichlorobenzenamine |
| 2,4,6-trichloraniline |
| sym-Trichloroaniline |
| EINECS 211-219-8 |
| 2,4,6-Trichlor-anilin |
| Aniline,2,4,6-trichloro |
| s-Trichloroaniline |
| MFCD00007663 |
| Benzenamine,2,4,6-trichloro |
 CAS#:142-04-1
CAS#:142-04-1 CAS#:95-51-2
CAS#:95-51-2 CAS#:18708-70-8
CAS#:18708-70-8 CAS#:529-23-7
CAS#:529-23-7 CAS#:351027-75-3
CAS#:351027-75-3 CAS#:84104-39-2
CAS#:84104-39-2 CAS#:1678-25-7
CAS#:1678-25-7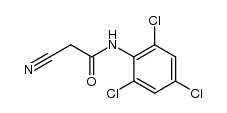 CAS#:24522-44-9
CAS#:24522-44-9 CAS#:799823-29-3
CAS#:799823-29-3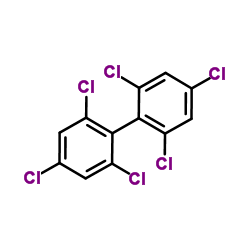 CAS#:33979-03-2
CAS#:33979-03-2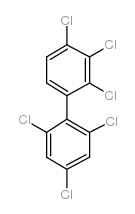 CAS#:59291-64-4
CAS#:59291-64-4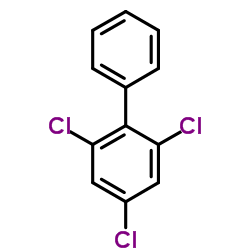 CAS#:35693-92-6
CAS#:35693-92-6 CAS#:32598-12-2
CAS#:32598-12-2 CAS#:56558-16-8
CAS#:56558-16-8 CAS#:31118-87-3
CAS#:31118-87-3 CAS#:59291-65-5
CAS#:59291-65-5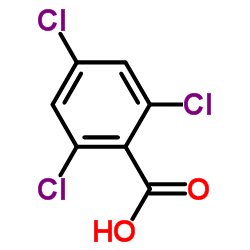 CAS#:50-43-1
CAS#:50-43-1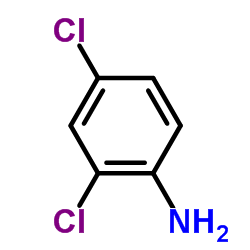 CAS#:554-00-7
CAS#:554-00-7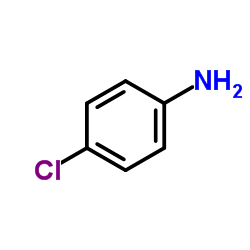 CAS#:106-47-8
CAS#:106-47-8
