2,4-Dichloroaniline
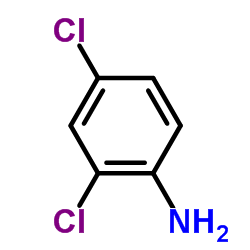
2,4-Dichloroaniline structure
|
Common Name | 2,4-Dichloroaniline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 554-00-7 | Molecular Weight | 162.017 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 242.1±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H5Cl2N | Melting Point | 59-62 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 100.2±21.8 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | 2,4-dichloroaniline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 242.1±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 59-62 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H5Cl2N |
| Molecular Weight | 162.017 |
| Flash Point | 100.2±21.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 160.979904 |
| PSA | 26.02000 |
| LogP | 2.74 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.614 |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble, |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H311-H331-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P273-P280-P301 + P310-P311-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R23/24/25;R33;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S36/37-S45-S60-S61-S28A |
| RIDADR | UN 3442 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BX2600000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2921499090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2921420090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2921420090 aniline derivatives and their salts VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Biodegradation of 2-chloroaniline, 3-chloroaniline, and 4-chloroaniline by a novel strain Delftia tsuruhatensis H1.
J. Hazard. Mater. 179(1-3) , 875-82, (2010) A new strain Delftia tsuruhatensis H1 able to degrade several chloroanilines (CAs) as individual compounds or a mixture was isolated from a CA-degrading mixed bacterial culture. The isolated strain co... |
|
|
Sensitivity of muscle satellite cells to pollutants: an in vitro and in vivo comparative approach.
Aquat. Toxicol. 53(3-4) , 247-63, (2001) Muscle satellite cells from rainbow trout were exposed in vitro to increasing concentrations of different xenobiotics: copper, dichloroaniline, prochloraz, nonyl-phenol polyethexylate. Mortality and p... |
|
|
Expression of delayed cell death (DCD) in the progeny of fish cells surviving 2,4-dichloroaniline (2,4-DCA) exposure.
Aquat. Toxicol. 63(3) , 207-19, (2003) Interest in and concern for the quality of the environment has prompted a great deal of research into methods of measuring and assessing changes in it. One problem of major interest is that of increas... |
| 2,4-Dichloroaniline |
| 2,4-di-Cl-aniline |
| 2,4-Dichloro Aniline |
| Benzenamine, 2,4-dichloro- |
| 1-Amino-2,4-dichlorobenzene |
| 2,4-Dichloranilin |
| 2,4-dichloro |
| EINECS 209-057-8 |
| 2,4-DCA |
| AURORA KA-688 |
| 2,4-dichloro-anilin |
| 1,5-dichloro-4-aminobenzene |
| o,p-Dichloroaniline |
| 2,4-dichloro-aniline |
| 4-Dichloroaniline |
| MFCD00007661 |
| aniline, 2,4-dichloro- |
| 2,4-dichloro-phenylamine |
 CAS#:36984-15-3
CAS#:36984-15-3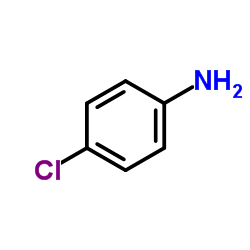 CAS#:106-47-8
CAS#:106-47-8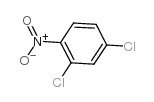 CAS#:611-06-3
CAS#:611-06-3 CAS#:13665-50-4
CAS#:13665-50-4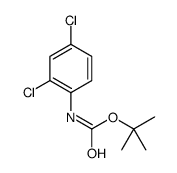 CAS#:296778-52-4
CAS#:296778-52-4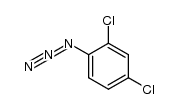 CAS#:1965-25-9
CAS#:1965-25-9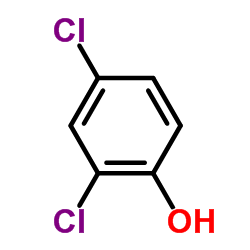 CAS#:120-83-2
CAS#:120-83-2 CAS#:116278-63-8
CAS#:116278-63-8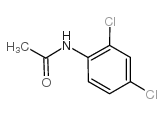 CAS#:6975-29-7
CAS#:6975-29-7 CAS#:111992-18-8
CAS#:111992-18-8 CAS#:5446-18-4
CAS#:5446-18-4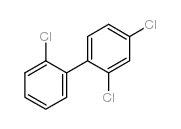 CAS#:37680-66-3
CAS#:37680-66-3 CAS#:50-84-0
CAS#:50-84-0 CAS#:3698-83-7
CAS#:3698-83-7 CAS#:41464-40-8
CAS#:41464-40-8 CAS#:34033-44-8
CAS#:34033-44-8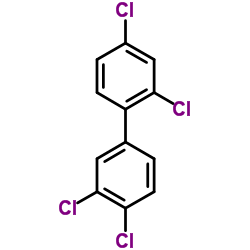 CAS#:32598-10-0
CAS#:32598-10-0 CAS#:35113-88-3
CAS#:35113-88-3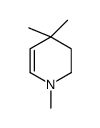 CAS#:35113-90-7
CAS#:35113-90-7
