Ethyl vanillate
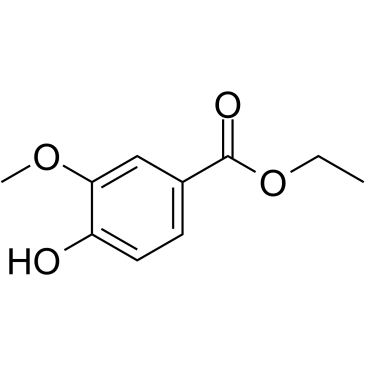
Ethyl vanillate structure
|
Common Name | Ethyl vanillate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 617-05-0 | Molecular Weight | 196.200 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 292.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12O4 | Melting Point | 43-45°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 122.4±15.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Ethyl vanillateEthyl Vanillate is a fungicidal agent. Ethyl Vanillate inhibits 17β-HSD2 with an IC50 1.3 µM[1][2]. |
| Name | Ethyl 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ethyl Vanillate is a fungicidal agent. Ethyl Vanillate inhibits 17β-HSD2 with an IC50 1.3 µM[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 1.3 µM (17β-HSD2)[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 292.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 43-45°C |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 196.200 |
| Flash Point | 122.4±15.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 196.073563 |
| PSA | 55.76000 |
| LogP | 2.07 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.528 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 22-36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | YW5425000 |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
|
~% 
Ethyl vanillate CAS#:617-05-0 |
| Literature: US6638928 B1, ; |
|
~% 
Ethyl vanillate CAS#:617-05-0
Detail
|
| Literature: US2010/121110 A1, ; Page/Page column 5-8 ; |
|
~81% 
Ethyl vanillate CAS#:617-05-0 |
| Literature: Kumar, Rakesh; Ramachandran, Uma; Srinivasan, Krishnamoorthy; Ramarao, Poduri; Raichur, Suryaprakash; Chakrabarti, Ranjan Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2005 , vol. 13, # 13 p. 4279 - 4290 |
|
~74% 
Ethyl vanillate CAS#:617-05-0 |
| Literature: Lee, Jong Chan; Choi, Youngsup Synthetic Communications, 1998 , vol. 28, # 11 p. 2021 - 2026 |
|
~88% 
Ethyl vanillate CAS#:617-05-0 |
| Literature: Lee, Jong Chan; Song, In-Goul; Park, Jin Young Synthetic Communications, 2002 , vol. 32, # 14 p. 2209 - 2213 |
|
~% 
Ethyl vanillate CAS#:617-05-0 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 37, p. 3160 - 3163 |
|
~% 
Ethyl vanillate CAS#:617-05-0 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 37, p. 3160 - 3163 |
|
~% 
Ethyl vanillate CAS#:617-05-0 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 37, p. 3160 - 3163 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 6 | |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918990090. other carboxylic acids with additional oxygen function and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Verifying the botanical authenticity of commercial tannins through sugars and simple phenols profiles.
Food Chem. 206 , 274-83, (2016) Commercial tannins from several botanical sources and with different chemical and technological characteristics are used in the food and winemaking industries. Different ways to check their botanical ... |
|
|
Hydro- and solvothermolysis of kraft lignin for maximizing production of monomeric aromatic chemicals.
Bioresour. Technol. 203 , 142-9, (2016) The hydro-/solvothermolysis of kraft lignin using water and ethanol as a solvent were investigated in this study. The effect of the water-to-ethanol ratio on the yields of monomeric aromatic chemicals... |
| 3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid ethyl ester |
| Ethyl vanillate |
| Ethyl 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate |
| EINECS 210-503-9 |
| Benzoic acid,4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-,ethyl ester |
| Benzoic acid, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-, ethyl ester |
| 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid ethyl ester |
| 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-ethyl benzoate |
| VANILLIC ACID,ETHYL ESTER |
| Ethyl-4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzolcarboxylat |
| ethyl-3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzoate |
| MFCD00017269 |




 CAS#:100377-63-7
CAS#:100377-63-7 CAS#:1486-53-9
CAS#:1486-53-9 CAS#:7152-90-1
CAS#:7152-90-1 CAS#:196194-41-9
CAS#:196194-41-9 CAS#:97966-31-9
CAS#:97966-31-9![5-[5-[4-(4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-yl)-2-methoxyphenoxy]pentyl]-3-methyl-1,2-oxazole structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/111/98033-66-0.png) CAS#:98033-66-0
CAS#:98033-66-0
