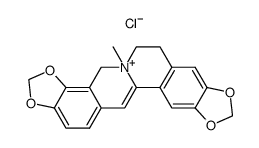
Coptisine chloride

Coptisine chloride structure
|
Common Name | Coptisine chloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6020-18-4 | Molecular Weight | 355.772 | |
| Density | 1.51g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 601.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H14ClNO4 | Melting Point | >258ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 190.4ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Coptisine chlorideCoptisine chloride is an alkaloid from Chinese goldthread, and acts as an efficient uncompetitive IDO inhibitor with a Ki value of 5.8 μM and an IC50 value of 6.3 μM. |
| Name | Coptisine Chloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Coptisine chloride is an alkaloid from Chinese goldthread, and acts as an efficient uncompetitive IDO inhibitor with a Ki value of 5.8 μM and an IC50 value of 6.3 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IDO:6.3 μM (IC50) IDO:5.8 μM (Ki) |
| In Vitro | Coptisine chloride is an efficient uncompetitive IDO inhibitor with a Ki value of 5.8 μM and an IC50 value of 6.3 μM[1]. Coptisine (0.1-100 μM) inhibits the proliferation of A549, H460, H2170, MDA-MB-231 and HT-29 cells, with IC50s of 18.09, 29.50, 21.60, 20.15 and 26.60 µM, respectively. Coptisine (12.5, 25, 50 μM) upregulates the expression of pH2AX and p21, reduces expression of cyclin B1, cdc2, and cdc25C, and induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis of A549 cells in a concentration-dependent manner. Coptisine (12.5, 25, 50 μM) also induces mitochondrial dysfunction and activates caspases activities in A549 cells. Furthermore, Coptisine (50 μM) increases ROS levels in a time-dependent manner (0.5, 1, 2, 4, 12, and 24 h)[3]. |
| In Vivo | Coptisine shows increased toxicity in mice in a concentration dependent manner, with LD50 value of 880.18 mg/kg. Coptisine (154 mg/kg/day, 90 days) shows no toxicity on SD rats. Coptisine (23.35, 46.7, 70.05 mg/kg, p.o.) dose-dependently decreases the levels of TC, TG, and LDL-c and increases HDL-c content in serum of hamsters to different degree, slows down weight gain induced by the HFHC diet, and raises the level of cholesterol and TBA in feces dose-dependently in hamsters. Coptisine (70.05 mg/kg, p.o.) suppresses HMGCR protein expression level and induces the protein expression of SREBP-2, LDLR, and CYP7A1 involved in cholesterol metabolism[2]. |
| Cell Assay | A 100-mM concentration of Coptisine is dissolved in DMSO, and subsequent concentrations ranging between 100 and 0.1 µM are prepared by diluting with cell culture medium. The final DMSO concentration used is less than 0.1% in every treatment. MTT assay is performed to assess cell proliferation effect of Coptisine. Briefly, 2500 cells/well are seeded in 96-well plate containing DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. A series of Coptisine concentrations are added and incubated for 48 h in the presence or absence of 5-mM NAC. After 48 h of incubation, 15 µL of MTT (5 mg/mL) is added to each well and incubated at 37°C for 4 h. Then, the supernatant is removed and 150 µL of DMSO is added to each well to dissolve the crystals. The absorbance is measured at 595 nm by Spectramax M4 plate reader[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] The acute toxicity of Coptisine is tested on Kunming mice, 10 mice in each group (half each males and females). Coptisine is dissolved in distilled water and prepared for administration with eight doses (482.5, 579, 694, 833, 1,000, 1,200, 1,440, and 1,728 mg/kg). After oral administration, the reactions of each mouse including mortality are observed and recorded for 1 week to obtain the LD50 value of Coptisine. Rats[2] Forty SD rats are divided into the control and Coptisine groups (half each males and females) which are treated for 90 days. The animal dose is calculated by the human equivalent dose (HED) with the body surface area (BSA) normalization method. To determine the sub-chronic toxicity, the actual dosage of Coptisine on SD rats (154 mg/kg/day) is obtained using the maximum HED of Coptisine (25 mg/kg) for an adult (60 kg) as a reference. Rats in the control group are given the same volume of 0.9 % saline. In the whole experiment, all animals are fed a normal diet and water ad libitum. The general appearance and behavior of rats are recorded daily, their body weight is measured every 10 days, and clinical signs and mortality are observed twice daily. |
| References |
| Density | 1.51g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 601.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >258ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C19H14ClNO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 355.772 |
| Flash Point | 190.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 355.061127 |
| PSA | 40.80000 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.749 |
| Storage condition | Hygroscopic, Refrigerator, Under Inert Atmosphere |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Hazard Codes | N |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~79% 
Coptisine chloride CAS#:6020-18-4 |
| Literature: Valpuesta, Maria; Diaz, Amelia; Torres, Gregorio; Suau, Rafael Tetrahedron, 2002 , vol. 58, # 25 p. 5053 - 5059 |
|
~% 
Coptisine chloride CAS#:6020-18-4 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 58, # 25 p. 5053 - 5059 |
|
~% 
Coptisine chloride CAS#:6020-18-4 |
| Literature: Chinese Chemical Letters, , vol. 21, # 11 p. 1281 - 1282 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| 6,7-Dihydro[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g][1,3]dioxolo[7,8]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinolin-5-ium chloride |
| Coptisine chloride |
| Bis[1,3]benzodioxolo[5,6-a:4',5'-g]quinolizinium, 6,7-dihydro-, chloride |
| 6,7-dihydrobis[1,3]benzodioxolo[5,6-a:4',5'-g]quinolizinium chloride |
| [1,3]Benzodioxolo[5,6-a]-1,3-benzodioxolo[4,5-g]quinolizinium, 6,7-dihydro-, chloride (1:1) |
| 6,7-Dihydro[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g][1,3]dioxolo[7,8]isoquino[3,2-a]isoquinolin-5-ium chloride |
| Coptisine (chloride) |