Schisantherin A
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 18:36:24
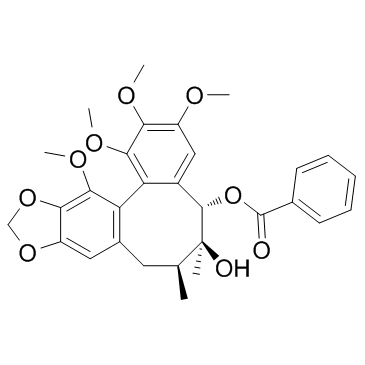
Schisantherin A structure
|
Common Name | Schisantherin A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 58546-56-8 | Molecular Weight | 536.570 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 675.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H32O9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 218.9±25.0 °C | |
Use of Schisantherin ASchisantherin A is a dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan isolated from the fruit of Schisandra sphenanthera. Schisantherin A inhibits p65-NF-κB translocation into the nucleus by IκBα degradation. |
| Name | Schisantherin A |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Schisantherin A is a dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan isolated from the fruit of Schisandra sphenanthera. Schisantherin A inhibits p65-NF-κB translocation into the nucleus by IκBα degradation. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
p65 |
| In Vitro | The concentrations of TNF-α and IL-6 in the supernatant of cells pretreated with 2.5 or 25 mg/L of Schisantherin A are significantly decreased compared to the LPS control group (p<0.05, p<0.01). The potential cytotoxicity of Schisantherin A is evaluated by the MTT assay after incubating cells for 24 h in the absence or presence of LPS, result shows cell viabilities are not affected by the cytokines at concentrations used (0.5, 2.5, 25 mg/L). RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells are pre-incubated with Schisantherin A for 1 h and then stimulated with 1 mg/L LPS for 12 h. Both LPS and samples are untreated in control group. After the cell culture media are collected, nitrite and PGE2 levels are determined, and Schisantherin A is found to reduce NO and PGE2 production in a dose-dependent manner[1]. |
| In Vivo | Schisantherin A, a dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan isolated from the fruit of Schisandra sphenanthera, has been reported to possess varied beneficial pharmacological effects. Schisantherin A protects lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in mice through inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Pretreatment with Schisantherin A markedly ameliorates LPS-induced histopathologic changes and decreases the levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in the BALF. In addition, the phosphorylation of NF-κB p65, IκB-α, JNK, ERK and p38 induced by LPS are suppressed by Schisantherin A. The lung wet/dry weight ratio is evaluated at 7 h after the intranasal instillation of LPS. The results show that there are no differences between control group and Schisantherin A (40 mg/kg) group (p>0.05). LPS causes a significant increase in lung wet/dry weight ratio (p<0.01) compared with the control group. Schisantherin A dose-dependently decreases the lung wet/dry weight ratio (p<0.05) compared to those in the LPS group[1]. |
| Cell Assay | The MTT assay is performed to measure cell viability. RAW 264.7 cells are mechanically scraped, seeded in 96-well plates at 4×105 cells/mL, and incubated in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator overnight. After 24 h, cells, treated with 50 μL of different concentrations of Schisantherin A (0-25 mg/L) for 1 h are then stimulated with 50 μL LPS for 18 h. Subsequently, 20 μL of 5 mg/mL MTT in FBS-free medium is added to each well, and the cells are incubated for 4 h. MTT is removed and resolved with 150 μL/well DMSO. The optical density is measured at 570 nm using a microplate reader. Concentrations are determined for three wells of each sample, and this experiment done in triplicate[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Male BALB/c mice, 6-8 weeks old, are used. All mice are randomly divided into six groups: control group, Schisantherin A (40 mg/kg) group, LPS group, Schisantherin A (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg)+LPS group, and Dexamethasone (DEX)+LPS group. DEX+LPS group is used as a positive control. Schisantherin A and DEX (5 mg/kg) are conducted intraperitoneally. Mice of control and LPS groups are given an equal volume of PBS. One hour later, after slightly anesthetized with an inhalation of diethyl ether, mice are instilled intranasally (i.n.) 10 μg LPS in 50 μL PBS to induce lung injury. Control mice are given 50 μL PBS instead of LPS. All mice are alive after 7 h of LPS treatment[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 675.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C30H32O9 |
| Molecular Weight | 536.570 |
| Flash Point | 218.9±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 536.204651 |
| PSA | 101.91000 |
| LogP | 6.38 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.623 |
| Benzo[3',4']cycloocta[1',2':4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxole-5,6-diol, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1,2,3,13-tetramethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-, 5-benzoate |
| (5S,6S,7S)-6-Hydroxy-1,2,3,13-tetramethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3',4']cycloocta[1',2':4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl benzoate |
| Benzo[3',4']cycloocta[1',2':4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxole-5,6-diol, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1,2,3,13-tetramethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-, 5-benzoate, (5S,6S,7S)- |
| 6-Hydroxy-1,2,3,13-tetramethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3',4']cycloocta[1',2':4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl benzoate |
| SCHISANTHERINGOMISIN |
| 6-Hydroxy-1,2,3,13-tetramethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3,4]cycloocta[1,2-f][1,3]benzodioxol-5-yl benzoate |
| SchizantherinA |
| Schisantherin A |