Dimethyl oxalate
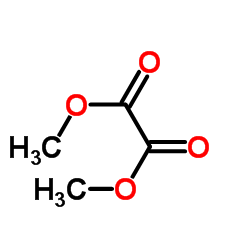
Dimethyl oxalate structure
|
Common Name | Dimethyl oxalate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 553-90-2 | Molecular Weight | 118.088 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 163.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H6O4 | Melting Point | 50-54 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 75.0±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | Dimethyl oxalate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 163.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 50-54 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 118.088 |
| Flash Point | 75.0±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 118.026611 |
| PSA | 52.60000 |
| LogP | -0.34 |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.1±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.391 |
| InChIKey | LOMVENUNSWAXEN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COC(=O)C(=O)OC |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, acids, bases, reducing agents. |
| Water Solubility | 60 G/L (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | 1759 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RO2850000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2917119000 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2917119000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2917119000 oxalic acid salts and esters VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
High activity and selectivity of Ag/SiO2 catalyst for hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate.
Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 46(24) , 4348-50, (2010) Ag/SiO(2) prepared by a sol-gel process is highly effective for selective gas-phase hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to corresponding alcohols. The catalysts are of great potential as industrially vi... |
|
|
Solvent feedstock effect: the insights into the deactivation mechanism of Cu/SiO2 catalysts for hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol.
Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 49(45) , 5195-7, (2013) The variation of the supports on the Cu/SiO2 catalyst plays an important role in the catalytic performance for hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate. The loss of silica in the form of tetramethoxysilane f... |
|
|
A1h NMR Pulse Gradient Spin-Echo (PGSE) Mass Transport Study of Dimethyl Oxalate and Ethylene Glycol: New Fuels for the DOFC. Suarez-Gustave S, et al.
Electrochem. Solid-State Let. 12(3) , 525-528, (2000)
|
| dimetyl oxalate |
| methyl ethanedioate |
| Oxalicdimethylester |
| oxalic acid dimethyl ester |
| CH3OCOCOOCH3 |
| DMO |
| Ethanedioic acid, dimethyl ester |
| EINECS 209-053-6 |
| Dimethyloxalate |
| dimethyl ethanedioate |
| METHYL OXALATE |
| oxalic acid diester |
| UNII-IQ3Q79344S |
| dimethyl oxolate |
| MFCD00008442 |
 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1 CAS#:79-37-8
CAS#:79-37-8 CAS#:624-91-9
CAS#:624-91-9 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2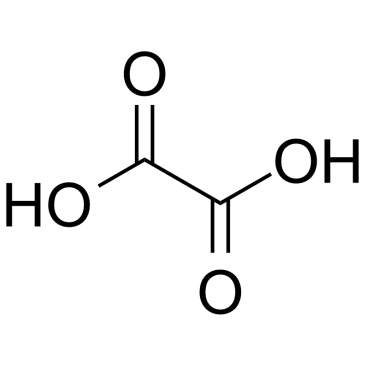 CAS#:144-62-7
CAS#:144-62-7 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9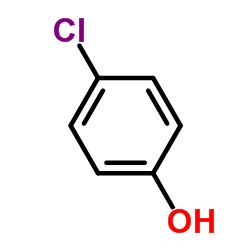 CAS#:106-48-9
CAS#:106-48-9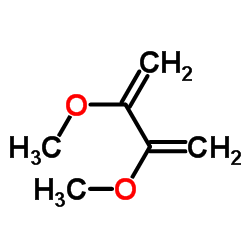 CAS#:3588-31-6
CAS#:3588-31-6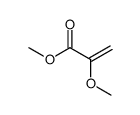 CAS#:7001-18-5
CAS#:7001-18-5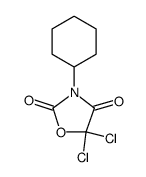 CAS#:91467-11-7
CAS#:91467-11-7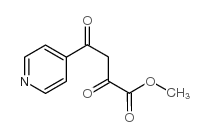 CAS#:374063-91-9
CAS#:374063-91-9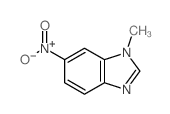 CAS#:5381-79-3
CAS#:5381-79-3 CAS#:5381-78-2
CAS#:5381-78-2 CAS#:39757-31-8
CAS#:39757-31-8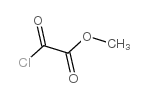 CAS#:5781-53-3
CAS#:5781-53-3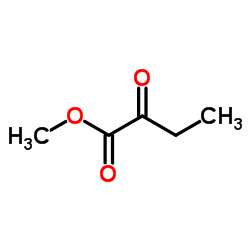 CAS#:3952-66-7
CAS#:3952-66-7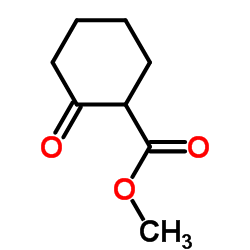 CAS#:41302-34-5
CAS#:41302-34-5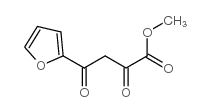 CAS#:374063-90-8
CAS#:374063-90-8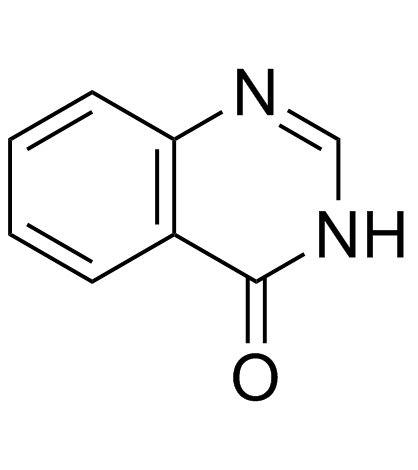 CAS#:491-36-1
CAS#:491-36-1 CAS#:39757-36-3
CAS#:39757-36-3
