Narasin
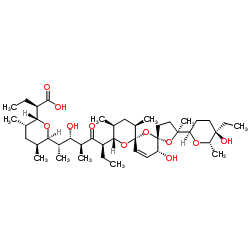
Narasin structure
|
Common Name | Narasin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 55134-13-9 | Molecular Weight | 765.025 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 842.5±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C43H72O11 | Melting Point | 98-100° | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 242.3±27.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of NarasinNarasin is a cationic ionophore and coccidiostat agent. Narasin inhibits NF-κB signaling and induces tumor cells apoptosis. Narasin has antimicrobial and anticancer activity[1]. |
| Name | narasin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Narasin is a cationic ionophore and coccidiostat agent. Narasin inhibits NF-κB signaling and induces tumor cells apoptosis. Narasin has antimicrobial and anticancer activity[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 842.5±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 98-100° |
| Molecular Formula | C43H72O11 |
| Molecular Weight | 765.025 |
| Flash Point | 242.3±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 764.507446 |
| PSA | 161.21000 |
| LogP | 6.59 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.545 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
| Risk Phrases | 28 |
| Safety Phrases | 28-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VO8640000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
|
Rapid method for the simultaneous determination of six ionophores in feed by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry.
J. AOAC Int. 95(4) , 1016-22, (2012) A simple and highly sensitive LC/MS method was developed for the simultaneous determination of six ionophores--lasalocid, monensin, laidlomycin, maduramycin, salinomycin, and narasin--in feed. The pro... |
|
|
Sensitivity of Eimeria field isolates in the United States: responses of nicarbazin-containing anticoccidials.
Poult. Sci. 87(9) , 1760-7, (2008) A series of studies were conducted to assess the drug sensitivity of 26 coccidial field isolates to the anticoccidial effects of nicarbazin (NIC) and narasin + NIC (NAR + NIC). Isolates were collected... |
|
|
Determination of narasin and monensin in bovine, swine, and chicken tissues by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry: first action 2011.24.
J. AOAC Int. 95(4) , 959-91, (2012) The single-laboratory validation (SLV) of an LC-MS/MS method for determination and confirmation of two ionophores, narasin and monensin, in animal tissues is described. The data demonstrated linearity... |
| c7819b |
| Narasul |
| monteban |
| (4S)-4-Methylsalinomycin |
| UNII:DZY9VU539P |
| (2R)-2-{(2R,3S,5S,6R)-6-[(2S,3S,4S,6R)-6-{(2S,5S,7R,9S,10S,12R,15R)-2-[(2R,5R,6S)-5-Ethyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]-15-hydroxy-2,10,12-trimethyl-1,6,8-trioxadispiro[4.1.5.3]pentadec-13-en-9-yl}-3-hydroxy-4-methyl-5-oxooctan-2-yl]-3,5-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl}butanoic acid |
| 2H-Pyran-2-acetic acid, α-ethyl-6-[(1S,2S,3S,5R)-5-[(2S,5S,7R,9S,10S,12R,15R)-2-[(2R,5R,6S)-5-ethyltetrahydro-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-2H-pyran-2-yl]-15-hydroxy-2,10,12-trimethyl-1,6,8-trioxadispiro[4.1 .5.3]pentadec-13-en-9-yl]-2-hydroxy-1,3-dimethyl-4-oxoheptyl]tetrahydro-3,5-dimethyl-, (αR,2R,3S,5S,6R)- |
| Antibiotic A 28086 Factor A |
| Narasia A |
| Narasin |
| antibioticc7819b |
| 4-methylsalinomycin |
| narasina |
| Salinomycin, 4-methyl-, (4S)- |
| (2R)-2-{(2R,3S,5S,6R)-6-[(2S,3S,4S,6R)-6-{(2S,5S,7R,9S,10S,12R,15R)-2-[(2R,5R,6S)-5-Ethyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]-15-hydroxy-2,10,12-trimethyl-1,6,8-trioxadispiro[4.1.5.3]pentadec-13-en-9-yl}-3-hydroxy-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-octanyl]-3,5-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl}butanoic acid |
| 2H-pyran-2-acetic acid, α-ethyl-6-[(1S,2S,3S,5R)-5-[(2S,5S,7R,9S,10S,12R,15R)-2-[(2R,5R,6S)-5-ethyltetrahydro-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-2H-pyran-2-yl]-15-hydroxy-2,10,12-trimethyl-1,6,8-trioxadispiro[4.1.5.3]pentadec-13-en-9-yl]-2-hydroxy-1,3-dimethyl-4-oxoheptyl]tetrahydro-3,5-dimethyl-, (αR,2R,3S,5S,6R)- |