BML-210
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 18:19:54
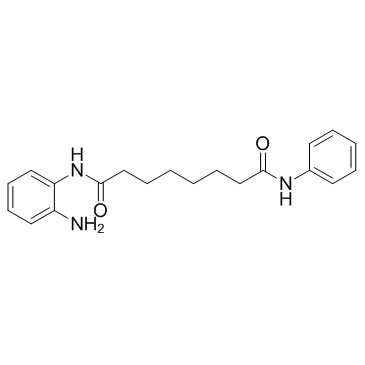
BML-210 structure
|
Common Name | BML-210 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 537034-17-6 | Molecular Weight | 339.431 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 632.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H25N3O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 336.3±27.3 °C | |
Use of BML-210BML-210 is a novel HDAC inhibitor, and its mechanism of action has not been characterized.IC50 value: 5 μM[1]Target: HDAC4In vitro: Cell cycle analysis indicated that HeLa cell treatment with 20 and 30 μM concentration of BML-210 increased the proportion of cells in G0/G1 phase, and caused accumulation in subG1, indicating that the cells are undergoing apoptosis[2]. BML-210 inhibits the growth of NB4 cells in dose- and time-dependent manner[3].In vivo: |
| Name | bml-210 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | BML-210 is a novel HDAC inhibitor, and its mechanism of action has not been characterized.IC50 value: 5 μM[1]Target: HDAC4In vitro: Cell cycle analysis indicated that HeLa cell treatment with 20 and 30 μM concentration of BML-210 increased the proportion of cells in G0/G1 phase, and caused accumulation in subG1, indicating that the cells are undergoing apoptosis[2]. BML-210 inhibits the growth of NB4 cells in dose- and time-dependent manner[3].In vivo: |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
HDAC4:MEF2 |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 632.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H25N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 339.431 |
| Flash Point | 336.3±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 339.194672 |
| PSA | 84.22000 |
| LogP | 2.58 |
| Appearance of Characters | white solid |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.633 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Hazard Statements | H413 |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor BML-210 Influences Gene and Protein Expression in Human Promyelocytic Leukemia NB4 Cells via Epigenetic Reprogramming.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 , 18252-69, (2015) Today, cancer is understood as an epigenetic as well as genetic disease. The main epigenetic hallmarks of the cancer cell are DNA methylation and histone modifications. Proteins such as histone deacet... |
| BML-210 |
| N'-(2-aminophenyl)-N-phenyloctanediamide |
| N-(2-Aminophenyl)-N'-phenyloctanediamide |
| Octanediamide, N-(2-aminophenyl)-N-phenyl- |