N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine
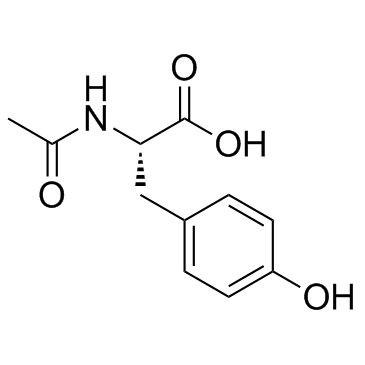
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine structure
|
Common Name | N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 537-55-3 | Molecular Weight | 223.225 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 531.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H13NO4 | Melting Point | 149-152 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 275.1±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of N-Acetyl-L-tyrosineN-Acetyl-L-tyrosine originates from tyrosine through an AA acetylase, is associated with aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency and tyrosinemia I. |
| Name | N-acetyl-L-tyrosine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine originates from tyrosine through an AA acetylase, is associated with aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency and tyrosinemia I. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 531.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 149-152 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C11H13NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 223.225 |
| Flash Point | 275.1±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 223.084457 |
| PSA | 86.63000 |
| LogP | 0.04 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.577 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H318 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338 + P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R41 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Surfactants, aromatic and isoprenoid compounds, and fatty acid biosynthesis inhibitors suppress Staphylococcus aureus production of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 , 1898-906, (2009) Menstrual toxic shock syndrome is a rare but potentially life-threatening illness manifest through the actions of Staphylococcus aureus toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1). Previous studies have sho... |
|
|
Detection of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease by NMR spectroscopic fingerprinting of urine.
Kidney Int. 79(11) , 1244-53, (2011) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a frequent cause of kidney failure; however, urinary biomarkers for the disease are lacking. In a step towards identifying such markers, we used... |
|
|
Newborn screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia: additional steroid profile using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92(7) , 2581-9, (2007) Neonatal screening programs for congenital adrenal hyperplasia (21-CAH) using an immunoassay for 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP) generate a high rate of positive results attributable to physiolog... |
| (2S)-2-(acetylamino)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
| L-Tyrosine, N-acetyl- |
| Ac-L-Tyr-OH |
| acetyl tyrosine |
| N-AC-L-TYR |
| (2S)-2-acetamido-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
| N-Ac-Tyr |
| EINECS 208-671-3 |
| n-acetyl-l-tyrosin |
| AC-TYR-OH |
| N-Acetyltyrosine |
| N-acetyl-L-Tyr |
| Ac-L-Tyrosine |
| A-L-Tyr-OH |
| AC-TYROSINE |
| (2S)-2-Acetylamino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
| Tyrosine, N-acetyl-, L- |
| L-N-acetyl-Tyrosine |
| N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine |
| ACETYL-L-TYROSINE |
| N-ACEYL-L-TYROSINE |
| MFCD00037190 |
 CAS#:108-24-7
CAS#:108-24-7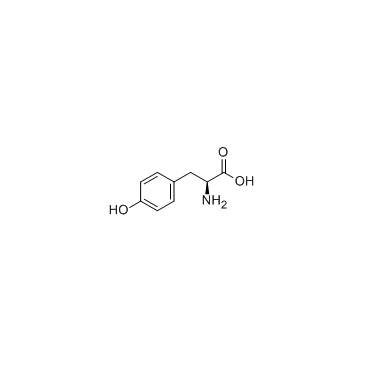 CAS#:60-18-4
CAS#:60-18-4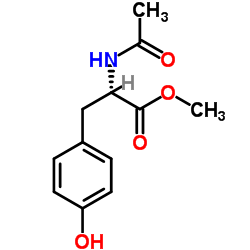 CAS#:2440-79-1
CAS#:2440-79-1 CAS#:64896-33-9
CAS#:64896-33-9 CAS#:38243-39-9
CAS#:38243-39-9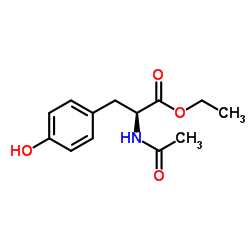 CAS#:840-97-1
CAS#:840-97-1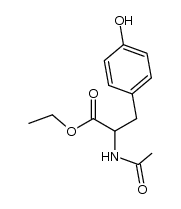 CAS#:30697-69-9
CAS#:30697-69-9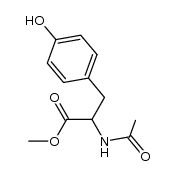 CAS#:23525-90-8
CAS#:23525-90-8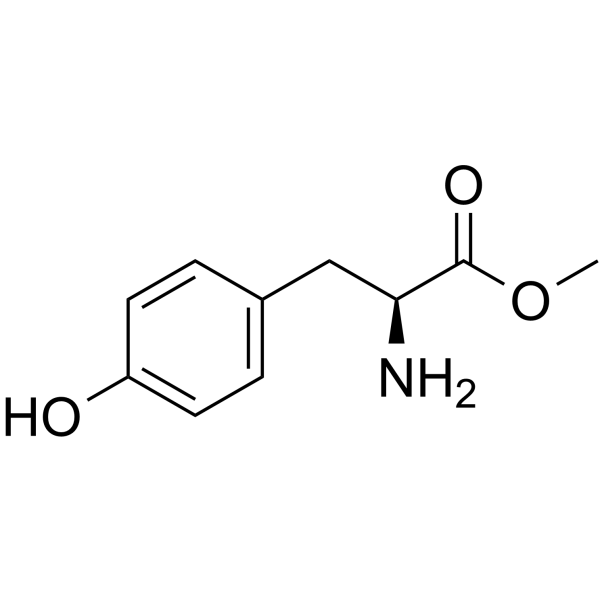 CAS#:1080-06-4
CAS#:1080-06-4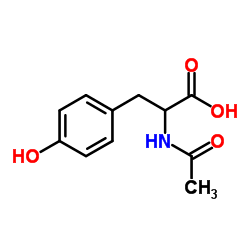 CAS#:2901-77-1
CAS#:2901-77-1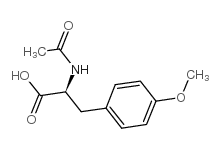 CAS#:28047-05-4
CAS#:28047-05-4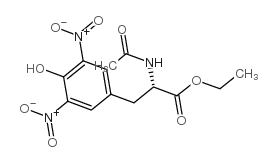 CAS#:29358-99-4
CAS#:29358-99-4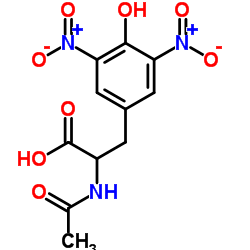 CAS#:20767-00-4
CAS#:20767-00-4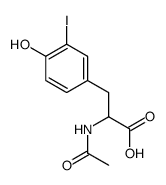 CAS#:1023-47-8
CAS#:1023-47-8 CAS#:1027-28-7
CAS#:1027-28-7 CAS#:32795-52-1
CAS#:32795-52-1
