DICLOFOP-METHYL
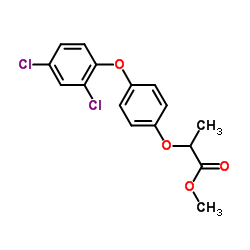
DICLOFOP-METHYL structure
|
Common Name | DICLOFOP-METHYL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 51338-27-3 | Molecular Weight | 341.186 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 408.0±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H14Cl2O4 | Melting Point | 39-41°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 150.3±27.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of DICLOFOP-METHYLDiclofop-methyl, a common post-emergence herbicide, is widely used in agriculture production. Diclofop-methyl increases the proton permeability of isolated oat-root tonoplast[1][2]. |
| Name | diclofop-methyl |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Diclofop-methyl, a common post-emergence herbicide, is widely used in agriculture production. Diclofop-methyl increases the proton permeability of isolated oat-root tonoplast[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Diclofop-methyl (1 micromolar) significantly reduced the steady-state H(+) gradient generated in the presence of ATP[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 408.0±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 39-41°C |
| Molecular Formula | C16H14Cl2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 341.186 |
| Flash Point | 150.3±27.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 340.026917 |
| PSA | 44.76000 |
| LogP | 4.24 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.562 |
| InChIKey | BACHBFVBHLGWSL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COC(=O)C(C)Oc1ccc(Oc2ccc(Cl)cc2Cl)cc1 |
| Water Solubility | 0.005 g/100 mL |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H317-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P280-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R43;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S24-S37-S60-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 |
| RTECS | UF1180000 |
| HS Code | 2918990025 |
|
~% 
DICLOFOP-METHYL CAS#:51338-27-3 |
| Literature: US4531969 A1, ; |
|
~91% 
DICLOFOP-METHYL CAS#:51338-27-3 |
| Literature: Zeitschrift fuer Naturforschung, Teil B: Anorganische Chemie, Organische Chemie, , vol. 35, # 3 p. 366 - 371 |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918990090. other carboxylic acids with additional oxygen function and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Characterisation of target-site resistance to ACCase-inhibiting herbicides in the weed Alopecurus myosuroides (black-grass).
Pest Manag. Sci. 59(2) , 190-201, (2003) Resistance to aryloxyphenoxypropionate (AOPP), cyclohexanedione (CHD) and phenylurea herbicides was determined in UK populations of Alopecurus myosuroides Huds. Two populations (Oxford AA1, Notts. A1)... |
|
|
Genetic control of a cytochrome P450 metabolism-based herbicide resistance mechanism in Lolium rigidum.
Heredity (Edinb.) 106(5) , 817-24, (2011) The dynamics of herbicide resistance evolution in plants are influenced by many factors, especially the biochemical and genetic basis of resistance. Herbicide resistance can be endowed by enhanced rat... |
|
|
Recurrent selection with reduced herbicide rates results in the rapid evolution of herbicide resistance in Lolium rigidum.
Theor. Appl. Genet. 110(6) , 1154-66, (2005) There has been much debate regarding the potential for reduced rates of herbicide application to accelerate evolution of herbicide resistance. We report a series of experiments that demonstrate the po... |
| Propanoic acid, 2-[4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenoxy]-, methyl ester |
| DICLOFOP-METHYL |
| Hoelon |
| 2-[4-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)phenoxy]propanoic Acid Methyl Ester |
| Hoe-grass |
| Illoxan |
| Diclofop methyl ester |
| MFCD00128052 |
| Diclofop, methyl ester |
| EINECS 257-141-8 |
| diclofop methyl |
| Methyl 2-[4-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)phenoxy]propionate |
| rac-methyl (2R)-2-[4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenoxy]propanoate |
| Hoegrass |
| methyl (RS)-2-[4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenoxy]propionate |
| Methyl 2-[4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenoxy]propanoate |
| METHYL (RS)-2-(4-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENOXY)PHENOXY)PROPIONATE |

 CAS#:40843-25-2
CAS#:40843-25-2 CAS#:75021-71-5
CAS#:75021-71-5
