2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid
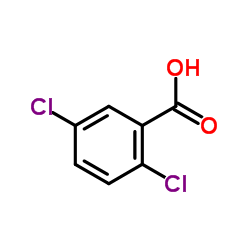
2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 50-79-3 | Molecular Weight | 191.012 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 301.0±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H4Cl2O2 | Melting Point | 151-154 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 135.8±22.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | 2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 301.0±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 151-154 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H4Cl2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 191.012 |
| Flash Point | 135.8±22.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 189.958832 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 2.97 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.599 |
| Stability | Stable. |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 19 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DG6825000 |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916399090 other aromatic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
[Oxidative dehalogenation of 2-chloro- and 2,4-dichlorobenzoates by Pseudomonas aeruginosa].
Mikrobiologiia 62(5) , 887-96, (1993) The strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa 142 isolated from the utilising PSBs bacterial association was capable of growth on 2-chloro- and 2,4-dichlorobenzoates as sole carbon sources, but it did not utilize... |
|
|
Degradation of 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid by Pseudomonas aeruginosa JB2 at low oxygen tensions.
Biodegradation 6(1) , 39-46, (1995) From long-term chemostat experiments, variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa JB2 were obtained which exhibited altered properties with respect to the metabolism of 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid (2,5-DBA). Thus... |
|
|
Quantitation in gradient high performance liquid chromatography/inductively coupled mass spectrometry investigated using diclofenac and chlorpromazine.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 16(4) , 245-7, (2002) The use of directly coupled high performance liquid chromatography/inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (HPLC/ICPMS) employing chlorine ((35)Cl/(37)Cl) detection has been investigated with res... |
| 2,5-dichlorobenzoicacid |
| MFCD00002416 |
| RARECHEM AL BO 0355 |
| EINECS 200-065-7 |
| 3-fluoro-4-nitrobenzoic acide |
| 5-Dichlorobenzoic acid |
| 1,2-DICHLOROBENZENE PESTANAL |
| 2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid |
| 2,4-DIETHOXY BENZALDEHYDE |
| Benzoic acid, 2,5-dichloro- |
| 2,5-dichloro-benzoicaci |
| 2,5-DBA |
| Benzoic acid,2,5-dichloro |
| 2,5-Dichlor-benzoesaeure |
| Irsogladine Impurity 2 |
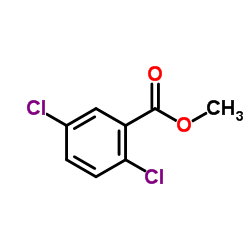 CAS#:2905-69-3
CAS#:2905-69-3 CAS#:108-98-5
CAS#:108-98-5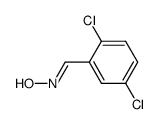 CAS#:80959-18-8
CAS#:80959-18-8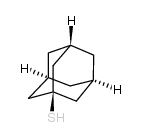 CAS#:34301-54-7
CAS#:34301-54-7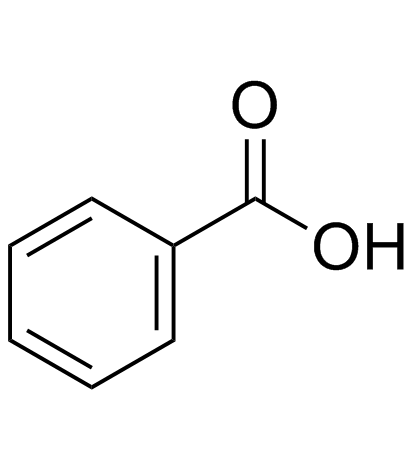 CAS#:65-85-0
CAS#:65-85-0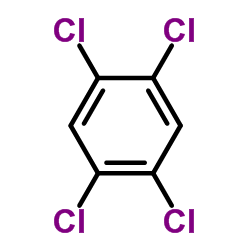 CAS#:95-94-3
CAS#:95-94-3 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9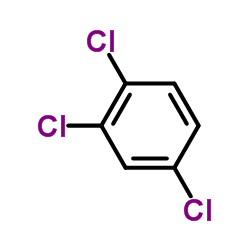 CAS#:120-82-1
CAS#:120-82-1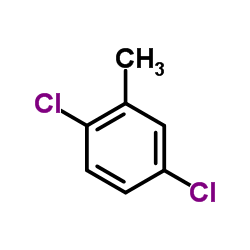 CAS#:19398-61-9
CAS#:19398-61-9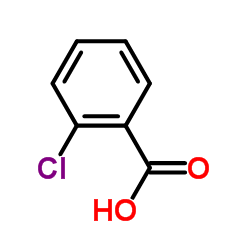 CAS#:118-91-2
CAS#:118-91-2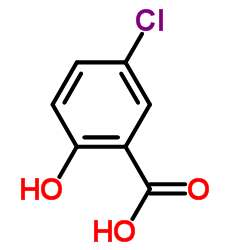 CAS#:321-14-2
CAS#:321-14-2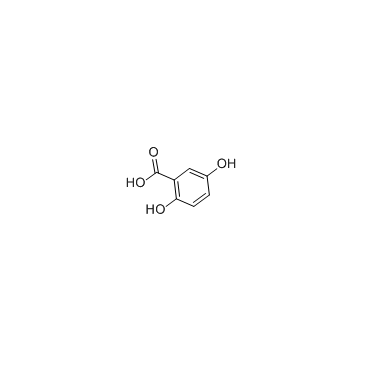 CAS#:490-79-9
CAS#:490-79-9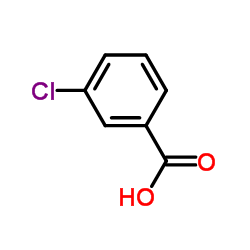 CAS#:535-80-8
CAS#:535-80-8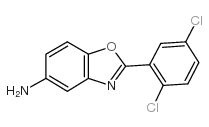 CAS#:293737-84-5
CAS#:293737-84-5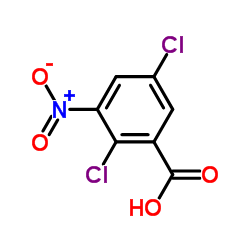 CAS#:88-86-8
CAS#:88-86-8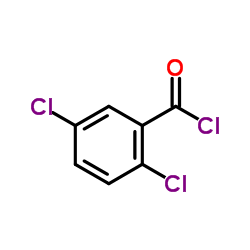 CAS#:2905-61-5
CAS#:2905-61-5 CAS#:89-75-8
CAS#:89-75-8 CAS#:7286-84-2
CAS#:7286-84-2 CAS#:5980-26-7
CAS#:5980-26-7
