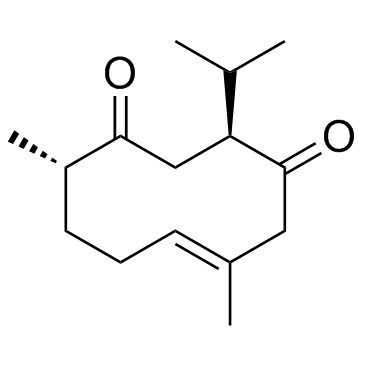
Curcumol

Curcumol structure
|
Common Name | Curcumol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4871-97-0 | Molecular Weight | 236.350 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 334.5±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H24O2 | Melting Point | 141-142ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 134.7±22.1 °C | |
Use of CurcumolCurcumol is a sesquiterpene originally isolated from curcuma rhizomes; shows anticancer activities both in vitro and in vivo.IC50 value:Target: Anticancer natural compoundin vitro: Curcumol exhibited time- and concentration-dependent anti-proliferative effects in SPC-A-1 human lung adenocarcinoma cells with cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase while apoptosis-induction was also confirmed with flow cytometry and morphological analyses [1]. Curcumol-induced growth inhibition correlated with apoptosis induction as evidenced by Annexin V staining, and cleavage of caspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in HSC-T6. Suppression of the NF-κB translocation via inhibition of IκB-α phosphorylation by the curcumol led to the inhibition of expression of NF-κB-regulated gene, e.g. Bcl-xL and Bcl-2, in a PI3K-dependent manner, which is upstream of NF-κB activation [2]. Curcumol exhibits an inhibitory effect on receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclast differentiation with both bone marrow-derived macrophages and RAW264.7 cells in a dose-dependent manner [3].in vivo: Anti-neoplastic effects of curcumol were also confirmed in tumor bearing mice. Curcumol (60 mg/kg daily) significantly reduced tumor size without causing notable toxicity [1]. |
| Name | Curcumol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Curcumol is a sesquiterpene originally isolated from curcuma rhizomes; shows anticancer activities both in vitro and in vivo.IC50 value:Target: Anticancer natural compoundin vitro: Curcumol exhibited time- and concentration-dependent anti-proliferative effects in SPC-A-1 human lung adenocarcinoma cells with cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase while apoptosis-induction was also confirmed with flow cytometry and morphological analyses [1]. Curcumol-induced growth inhibition correlated with apoptosis induction as evidenced by Annexin V staining, and cleavage of caspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in HSC-T6. Suppression of the NF-κB translocation via inhibition of IκB-α phosphorylation by the curcumol led to the inhibition of expression of NF-κB-regulated gene, e.g. Bcl-xL and Bcl-2, in a PI3K-dependent manner, which is upstream of NF-κB activation [2]. Curcumol exhibits an inhibitory effect on receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclast differentiation with both bone marrow-derived macrophages and RAW264.7 cells in a dose-dependent manner [3].in vivo: Anti-neoplastic effects of curcumol were also confirmed in tumor bearing mice. Curcumol (60 mg/kg daily) significantly reduced tumor size without causing notable toxicity [1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 334.5±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 141-142ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C15H24O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 236.350 |
| Flash Point | 134.7±22.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 236.177628 |
| PSA | 29.46000 |
| LogP | 3.25 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.526 |
| InChIKey | QRMPRVXWPCLVNI-YYFQZIEXSA-N |
| SMILES | C=C1CC2(O)OC3(CC2C(C)C)C(C)CCC13 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 29321900 |
|
~98% 
Curcumol CAS#:4871-97-0 |
| Literature: Li, Xian; Wu, Lijun; Ji, Zhizong; Harigaya, Yoshihiro; Konda, Yaeko; et al. Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, 1988 , vol. 25, p. 1403 - 1406 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Isolation and identification of phase 1 metabolites of curcumol in rats.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38(11) , 2014-22, (2010) Curcumol is one of the major components of the essential oil of Curcuma wenyujin with the structure of a guaiane-type sesquiterpenoid hemiketal. It exhibits clear antitumor, antihepatic fibrosis, anti... |
|
|
Subunit-specific inhibition of glycine receptors by curcumol.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 343(2) , 371-9, (2012) Emerging evidence has suggested that inhibitory glycine receptors (GlyRs) are an important molecular target in the treatment of numerous neurological disorders. Rhizoma curcumae is a medicinal plant w... |
|
|
Chemical constituents from the radix of Curcuma wenyujin.
Fitoterapia 80(6) , 374-6, (2009) Phytochemical study on the ethanol extract of the radixes of Curcuma wenyujin Y. H. Chen et C. Ling led to the isolation of three new compounds curcuminol F (1) curcuminol G (2) and wenyujinoside (3) ... |
| 6H-3a,6-Epoxyazulen-6-ol, octahydro-3-methyl-8-methylene-5-(1-methylethyl)-, (3S,3aS,5S,8aS)- |
| (3S,3aS,5S,8aS)-3-methyl-8-methylidene-5-(propan-2-yl)octahydro-6H-3a,6-epoxyazulen-6-ol |
| (3S,3aS,5S,6R,8aS)-Octahydro-3-methyl-8-methylene-5-(1-methylethyl)-6H-3a,6-epoxyazulen-6-ol |
| (1S,2S,5S,9S)-9-Isopropyl-2-methyl-6-methylene-11-oxatricyclo[6.2.1.0]undecan-8-ol |