Estrone sulfate sodium
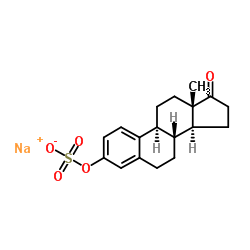
Estrone sulfate sodium structure
|
Common Name | Estrone sulfate sodium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 438-67-5 | Molecular Weight | 372.41 | |
| Density | 1.349 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H21NaO5S | Melting Point | 258-260°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Estrone sulfate sodiumEstrone sulfate, a biologically inactive form of estrogen, is a major circulating plasma estrogen that is converted into the biologically active estrogen, estrone (E1) by steroid sulfatase (STS). strone sulfate can be used for the research of breast cancer[1][2]. |
| Name | estrone sodium sulfate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Estrone sulfate, a biologically inactive form of estrogen, is a major circulating plasma estrogen that is converted into the biologically active estrogen, estrone (E1) by steroid sulfatase (STS). strone sulfate can be used for the research of breast cancer[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | T47D cells are stably transfected with SOAT and incubated under increasing concentrations of Estrone sulfate and estradiol at physiologically relevant concentrations. Cell proliferation is significantly increased by 1 nM estradiol as well as by Estrone sulfate with EC50 of 2.2 nM[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.349 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 258-260°C |
| Molecular Formula | C18H21NaO5S |
| Molecular Weight | 372.41 |
| Exact Mass | 372.100739 |
| PSA | 91.88000 |
| LogP | 4.03160 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335-H350 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P261-P305 + P351 + P338-P308 + P313 |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R45-36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-45-26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | KG8775000 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
|
Major active components in grapefruit, orange, and apple juices responsible for OATP2B1-mediated drug interactions.
J. Pharm. Sci. 102(1) , 280-8, (2013) We aimed to explore the major active components in grapefruit juice (GFJ), orange juice (OJ), and apple juice (AJ) that are responsible for OATP2B1-mediated drug interactions, by means of in vitro stu... |
|
|
Quantitative transporter proteomics by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry: addressing methodologic issues of plasma membrane isolation and expression-activity relationship.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 43(2) , 284-8, (2015) To predict transporter-mediated drug disposition using physiologically based pharmacokinetic models, one approach is to measure transport activity and relate it to protein expression levels in cell li... |
|
|
Inclusion of endogenous hormone levels in risk prediction models of postmenopausal breast cancer.
J. Clin. Oncol. 32(28) , 3111-7, (2014) Endogenous hormones are risk factors for postmenopausal breast cancer, and their measurement may improve our ability to identify high-risk women. Therefore, we evaluated whether inclusion of plasma es... |
| Estra-1(10),2,4-trien-17-one, 3-(sulfooxy)-, sodium salt (1:1) |
| Sodium 17-oxoestra-1(10),2,4-trien-3-yl sulfate |
| Estrone 3-sulfate sodium salt |
| Estrone sodium sulfate |
| Estrone sulfate sodium |
| Estrone-3-sulfate sodium salt |
| estrone sodium sulphate |
| Sodium estrone 3-sulfate |
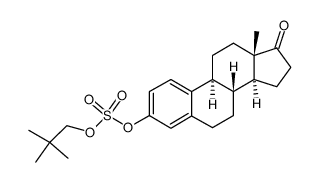 CAS#:878408-57-2
CAS#:878408-57-2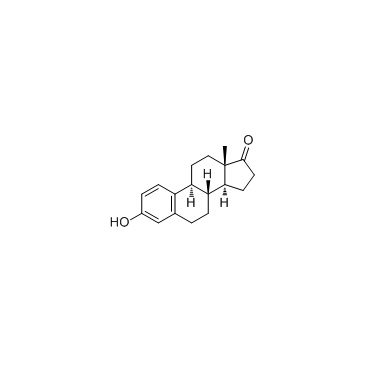 CAS#:53-16-7
CAS#:53-16-7