Monomethyl phthalate
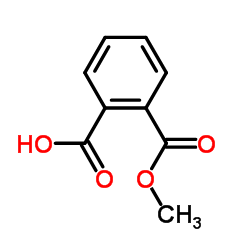
Monomethyl phthalate structure
|
Common Name | Monomethyl phthalate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4376-18-5 | Molecular Weight | 180.157 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 328.9±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O4 | Melting Point | 82-84 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 134.7±16.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Monomethyl phthalateMonomethyl phthalate is a phthalate metabolite. Monomethyl phthalate acts as a urinary biomarker of phthalates exposure and can be used as a standard for the determination of thyroid cancer and benign nodule[1]. |
| Name | methyl hydrogen phthalate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Monomethyl phthalate is a phthalate metabolite. Monomethyl phthalate acts as a urinary biomarker of phthalates exposure and can be used as a standard for the determination of thyroid cancer and benign nodule[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 328.9±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 82-84 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.157 |
| Flash Point | 134.7±16.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 180.042252 |
| PSA | 63.60000 |
| LogP | 1.13 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.556 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Feasibility of ultra-high performance liquid and gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry for accurate determination of primary and secondary phthalate metabolites in urine samples.
Anal. Chim. Acta 853 , 625-36, (2014) Phthalates (PAEs) are ubiquitous toxic chemical compounds. During the last few years, some phthalate metabolites (MPAEs) have been proposed as appropriate biomarkers in human urine samples to determin... |
|
|
Monitoring of PAEMs and beta-agonists in urine for a small group of experimental subjects and PAEs and beta-agonists in drinking water consumed by the same subjects.
J. Hazard. Mater. 277 , 169-79, (2014) This 5-month study contains two parts: (1) to monitor the concentrations of 11 phthalate esters metabolites (PAEMs) and two beta-agonists in human urine samples collected from a small group of consent... |
|
|
Phthalate Metabolites in Urine Samples from School Children in Taipei, Taiwan.
Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 69 , 202-7, (2015) In 2011, Taiwan authorities reported that two phthalates, including di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and di-iso-nonyl phthalate, were intentionally introduced into a variety of foods and beverages during t... |
| 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, monomethyl ester |
| Phthalic acid methyl ester |
| 2-methoxycarbonylbenzoic acid |
| 2-(Methoxycarbonyl)benzoic acid |
| Monomethyl phthalate |
| METHYL HYDROGEN PHTHALATE |
| phthalic acid, mono-methyl ester |
| MFCD00002466 |
| 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester |
| EINECS 224-476-6 |
| Phthalic acid monomethyl ester |
| mono-Methyl phthalate |
 CAS#:131-11-3
CAS#:131-11-3 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9 CAS#:610-97-9
CAS#:610-97-9 CAS#:73513-53-8
CAS#:73513-53-8 CAS#:1225-85-0
CAS#:1225-85-0 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1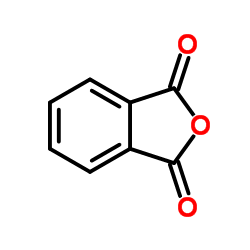 CAS#:85-44-9
CAS#:85-44-9 CAS#:4122-56-9
CAS#:4122-56-9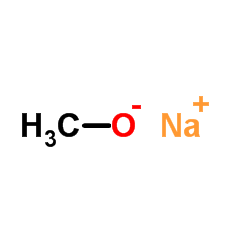 CAS#:124-41-4
CAS#:124-41-4 CAS#:78657-44-0
CAS#:78657-44-0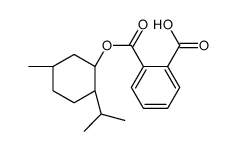 CAS#:33744-74-0
CAS#:33744-74-0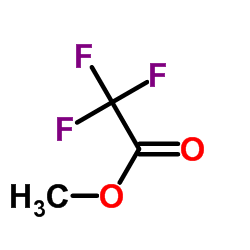 CAS#:431-47-0
CAS#:431-47-0 CAS#:88-99-3
CAS#:88-99-3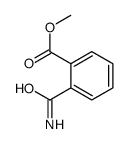 CAS#:90564-02-6
CAS#:90564-02-6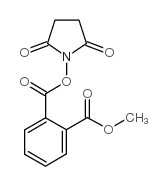 CAS#:438470-19-0
CAS#:438470-19-0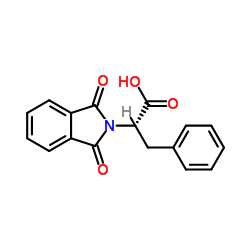 CAS#:5123-55-7
CAS#:5123-55-7![imino-[2-(2-methoxycarbonylphenyl)-2-oxo-ethylidene]azanium structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/163/18435-67-1.png) CAS#:18435-67-1
CAS#:18435-67-1 CAS#:520-03-6
CAS#:520-03-6
