IPA-3
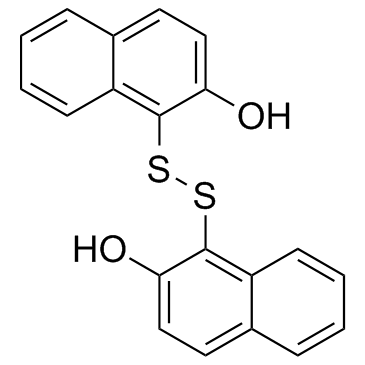
IPA-3 structure
|
Common Name | IPA-3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 42521-82-4 | Molecular Weight | 350.454 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 543.7±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H14O2S2 | Melting Point | 172℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 263.4±24.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of IPA-3IPA-3 is a selective non-ATP competitive PAK1 inhibitor with IC50 of 2.5 μM, and shows no inhibition to group II PAKs (PAKs 4-6). |
| Name | 1-[(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)disulfanyl]naphthalen-2-ol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | IPA-3 is a selective non-ATP competitive PAK1 inhibitor with IC50 of 2.5 μM, and shows no inhibition to group II PAKs (PAKs 4-6). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PAK1:2.5 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | IPA-3 inhibits Pak1 activation in part by binding covalently to the regulatory domain of Pak1. IPA-3 binds Pak1 covalently in a time- and temperature-dependent manner. IPA-3 prevents binding of the Pak1 activator Cdc42. IPA-3 binds directly to the Pak1 autoregulatory domain. IPA-3 reversibly inhibits PMA-induced membrane ruffling in cells[1]. IPA-3 (2 µM, 5 µM or 20 µM) reduces cell spreading in human primary Schwann and schwannoma cells. IPA-3 treatment significantly reduces the number of adherent Schwann and schwannoma cells in a dose-dependent manner[2]. IPA-3 is a non ATP-competitive, allosteric inhibitor of p21-activated kinase 1 (Pak1). PIR3.5 is the control compound of IPA-3. IPA-3 prevents Cdc42-stimulated Pak1 autophosphorylation on Thr423. IPA-3 also prevents sphingosine-dependent Pak1 autophosphorylation. IPA-3 does not target exposed cysteine residues on Pak1. The disulfide bond of IPA-3 is critical for inhibition of Pak1 and in vitro reduction by the reducing agent dithiothreitol (DTT) abolishes Pak1 inhibition by IPA-3. IPA-3 inhibits activation of Pak1 by diverse activators, but does not inhibit preactivated Pak1. IPA-3 inhibits PDGF-stimulated Pak activation in mouse embryonic fibroblasts[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Pak1 (150 nM final) is pre-incubated with MBP (8.3 μM), indicated proteins, and IPA-3 or DMSO in Kinase buffer for 20 minutes at 4°C. Cdc42-GTPγS (3.2 μM) is then added and the reaction is pre-equilibrated 10 minutes at 30°C. Kinase reactions are started by the addition of ATP (to 30 μM) containing [32P]ATP and are incubated 10 min and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. |
| Cell Assay | Human primary schwannoma cells are grown on 96 well plates for 2 days. Cells are left untreated or treated with 5 µM IPA-3, 20 µM IPA-3 or 20 µM PIR-3.5 for 24 hours. The MTS-solution is left on the cells for 3 hours, before the absorbance at 490 nm is measured. The experiments are conducted three times and mean and standard error of the mean is calculated with Excel. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 543.7±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 172℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C20H14O2S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 350.454 |
| Flash Point | 263.4±24.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 350.043518 |
| PSA | 91.06000 |
| LogP | 4.96 |
| Appearance of Characters | off-white to yellow |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.836 |
| InChIKey | RFAXLXKIAKIUDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Oc1ccc2ccccc2c1SSc1c(O)ccc2ccccc12 |
| Storage condition | Store at +4°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: >20mg/mL | Soluble in DMSO or ethanol. Insoluble in water. |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H318-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi,N |
| Risk Phrases | 41-50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-39-60-61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Essential role of endocytosis for interleukin-4-receptor-mediated JAK/STAT signalling.
J. Cell Sci. 128 , 3781-95, (2015) Many important signalling cascades operate through specialized signalling endosomes, but a corresponding mechanism has as yet not been described for hematopoietic cytokine receptors. Based on live-cel... |
|
|
PAK1 regulates RUFY3-mediated gastric cancer cell migration and invasion.
Cell Death Dis. 6 , e1682, (2015) Actin protrusion at the cell periphery is central to the formation of invadopodia during tumor cell migration and invasion. Although RUFY3 (RUN and FYVE domain containing 3)/SINGAR1 (single axon-relat... |
|
|
AP-2-associated protein kinase 1 and cyclin G-associated kinase regulate hepatitis C virus entry and are potential drug targets.
J. Virol. 89(8) , 4387-404, (2015) Hepatitis C virus (HCV) enters its target cell via clathrin-mediated endocytosis. AP-2-associated protein kinase 1 (AAK1) and cyclin G-associated kinase (GAK) are host kinases that regulate clathrin a... |
| 1,1'-Disulfanediyldi(2-naphthol) |
| 1,1'-Dithiodi-2-naphthol |
| UNII-3XFG6MQ9G2 |
| F0400-0044 |
| 2-Naphthalenol, 1,1'-dithiobis- |
| IPA-3 |
 CAS#:135-19-3
CAS#:135-19-3 CAS#:78315-87-4
CAS#:78315-87-4 CAS#:29601-60-3
CAS#:29601-60-3 CAS#:633-99-8
CAS#:633-99-8 CAS#:79347-46-9
CAS#:79347-46-9 CAS#:64-17-5
CAS#:64-17-5 CAS#:7705-08-0
CAS#:7705-08-0 CAS#:602-09-5
CAS#:602-09-5 CAS#:17096-15-0
CAS#:17096-15-0