Carnidazole
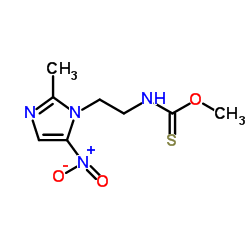
Carnidazole structure
|
Common Name | Carnidazole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 42116-76-7 | Molecular Weight | 244.271 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 422.8±51.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H12N4O3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 209.5±30.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of CarnidazoleCarnidazole is an antiprotozoal agent of the nitroimidazole class. Carnidazole is used for the research of Trichomonas infection[1]. |
| Name | O-methyl N-[2-(2-methyl-5-nitroimidazol-1-yl)ethyl]carbamothioate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Carnidazole is an antiprotozoal agent of the nitroimidazole class. Carnidazole is used for the research of Trichomonas infection[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Antiprotozoal[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 422.8±51.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C8H12N4O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 244.271 |
| Flash Point | 209.5±30.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 244.063004 |
| PSA | 116.99000 |
| LogP | 0.72 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.627 |
| InChIKey | OVEVHVURWWTPFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COC(=S)NCCn1c([N+](=O)[O-])cnc1C |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H317-H318 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | C |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | FD3912000 |
| HS Code | 2933290090 |
| HS Code | 2933290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933290090. other compounds containing an unfused imidazole ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Determination of the antitubercular drug PA-824 in rat plasma, lung and brain tissues by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry: application to a pharmacokinetic study.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 988 , 187-94, (2015) A selective, sensitive and high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-(ESI)MS/MS) method has been developed and validated for the quantification of the potent antitubercular d... |
|
|
In vitro nitroimidazole resistance of Trichomonas gallinae and successful therapy with an increased dosage of ronidazole in racing pigeons (Columba livia domestica).
J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 15(4) , 409-15, (1992) Six out of eight different Trichomonas gallinae strains isolated from racing pigeons proved to be resistant to the nitroimidazole drugs ronidazole, carnidazole and metronidazole. The minimal cytocidal... |
|
|
Structural characterization of drugs and oxygenated metabolites by laser microprobe mass spectrometry (LAMMA).
Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrom. 16(1-12) , 121-9, (1988) Laser microprobe mass analysis (LAMMA) was used for the structural characterization of polyfunctional drugs and their oxygenated metabolites, in particular the N-oxides. The spectra usually yield the ... |
| ME 108 |
| Spartrix |
| Carnidazole |
| [2-(2-Methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethyl]carbamothioic Acid O-Methyl Ester |
| Carbamothioic acid, N-[2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethyl]-, O-methyl ester |
| O-Methyl [2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethyl]carbamothioate |
| EINECS 255-663-0 |
| UNII-RH5KI819JG |