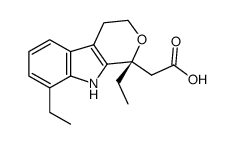
Etodolac
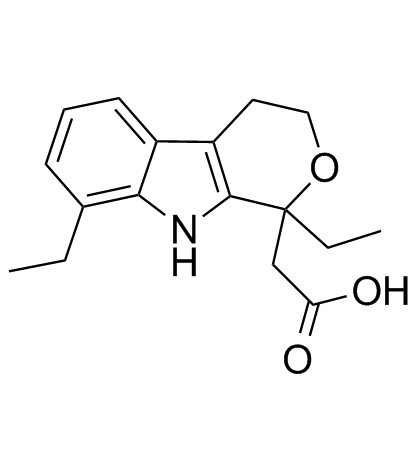
Etodolac structure
|
Common Name | Etodolac | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 41340-25-4 | Molecular Weight | 287.353 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 507.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H21NO3 | Melting Point | 145-1480C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 261.0±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of EtodolacEtodolac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory compound that is a non-selective inhibitor of COX (IC50=53.5 nM)IC50 value: 53.5 nMTarget: COX1; COX2Post-marketing studies demonstrated that etodolac inhibition of cyclooxygenase is somewhat COX-2 selective similar to celecoxib and other "COX-2 inhibitors." Unlike rofecoxib, both etodolac and celecoxib can fully inhibit COX-1 and are designated as having "preferential selectivity" toward COX-2. The (inactive against COX) r-enantiomer of etodolac inhibits beta-catenin levels in hepatoma cells. |
| Name | etodolac |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Etodolac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory compound that is a non-selective inhibitor of COX (IC50=53.5 nM)IC50 value: 53.5 nMTarget: COX1; COX2Post-marketing studies demonstrated that etodolac inhibition of cyclooxygenase is somewhat COX-2 selective similar to celecoxib and other "COX-2 inhibitors." Unlike rofecoxib, both etodolac and celecoxib can fully inhibit COX-1 and are designated as having "preferential selectivity" toward COX-2. The (inactive against COX) r-enantiomer of etodolac inhibits beta-catenin levels in hepatoma cells. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX-2:41 nM (IC50, in CHO cells) COX-1:∼50000 nM (IC50, in CHO cells) |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 507.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 145-1480C |
| Molecular Formula | C17H21NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 287.353 |
| Flash Point | 261.0±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 287.152130 |
| PSA | 62.32000 |
| LogP | 3.59 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.597 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic |
| Risk Phrases | R23/24/25;R40 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S36-S45-S26 |
| RIDADR | 3249 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UQ0360000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|
~% 
Etodolac CAS#:41340-25-4 |
| Literature: CHEMI SPA Patent: US2005/14953 A1, 2005 ; Location in patent: Page column 2 ; |
|
~% 
Etodolac CAS#:41340-25-4 |
| Literature: Cephalon, Inc. Patent: US2006/167259 A1, 2006 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 10 ; |
|
~% 
Etodolac CAS#:41340-25-4 |
| Literature: Cephalon, Inc. Patent: US2006/167259 A1, 2006 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 9 ; |
|
~% 
Etodolac CAS#:41340-25-4 |
| Literature: Demerson,C.A. et al. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1976 , vol. 19, p. 391 - 395 |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
A new analytical method to determine non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in surface water using in situ derivatization combined with ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
Talanta 129 , 552-9, (2014) Because of the high stability and potential toxic effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), it is important to closely monitor their concentrations in the environment using a sensitiv... |
|
|
Risk of peptic ulcer bleeding associated with Helicobacter pylori infection, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, low-dose aspirin, and antihypertensive drugs: a case-control study.
J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 30(2) , 292-8, (2015) The associations between antithrombotic or antihypertensive drugs and peptic ulcer bleeding (PUB) remain unknown, particularly in Asia, where Helicobacter pylori infection is prevalent. This study aim... |
|
|
A method for rapid screening of interactions of pharmacologically active compounds with albumin.
Anal. Chim. Acta 855 , 51-9, (2014) We determine the association constants for ligand-protein complex formation using the flow injection method. We carry out the measurements at high flow rates (F=1 mL min(-1)) of a carrier phase. There... |
| Etodolac |
| 1,8-Diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indole-1-acetic acid |
| etodolic acid |
| etodolacum [INN_la] |
| Ultrado |
| Etodolac [USAN:BAN:INN] |
| Lodine |
| Hypen |
| Tedolan |
| Zedolac |
| Pyrano[3,4-b]indole-1-acetic acid, 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro- |
| Etopen |
| UNII:2M36281008 |
| Etodlic acid |
| Edolan |
| MFCD00133313 |
| RAK-591 |
| Ramodar |
| (1,8-Diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl)acetic acid |