6-fluoroindole
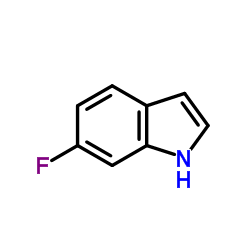
6-fluoroindole structure
|
Common Name | 6-fluoroindole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 399-51-9 | Molecular Weight | 135.14 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 258.0±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H6FN | Melting Point | 72-76 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 109.9±19.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 6-fluoroindole6-Fluoroindole is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
| Name | 6-Fluoroindole |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 6-Fluoroindole is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 6-Fluoroindole 在色氨酸双加氧酶抑制剂吡啶基-乙烯-吲哚的合成中用作试剂,吡啶基-乙烯-吲哚用作潜在的抗癌免疫调节剂。它还用作抗真菌剂和抗菌剂。此外,它还是一种有效的选择性 5-羟色胺再摄取抑制剂。除此之外,它还用作 HIV-1 附着的抑制剂。 |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 258.0±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 72-76 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H6FN |
| Molecular Weight | 135.14 |
| Flash Point | 109.9±19.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 135.048431 |
| PSA | 15.79000 |
| LogP | 2.19 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.646 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) inhibitors. 3-(2-(pyridyl)ethenyl)indoles as potential anticancer immunomodulators.
J. Med. Chem. 54 , 5320, (2011) Tryptophan catabolism mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is an important mechanism of peripheral immune tolerance contributing to tumoral immune resistance. IDO inhibition is thus an active... |
|
|
Ionization potentials of fluoroindoles and the origin of nonexponential tryptophan fluorescence decay in proteins.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127(11) , 4104-13, (2005) This work reports an explanation for the unusual monoexponential fluorescence decay of 5-fluorotryptophan (5FTrp) in single-Trp mutant proteins [Broos, J.; Maddalena, F.; Hesp, B. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc.... |
|
|
Discovery of novel N-β-D-xylosylindole derivatives as sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for the management of hyperglycemia in diabetes.
J. Med. Chem. 54 , 166, (2011) A novel series of N-linked β-D-xylosides were synthesized and evaluated for inhibitory activity against sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) in a cell-based assay. Of these, the 4-chloro-3... |
| 6-FLUOROINDOLE FOR SYNTHESIS 25 G |
| 6-Fluoroindole |
| 6-fluoro indole |
| 6-FLUORO-2-IODOBENZALDEHYDE |
| 6-Fluoro-1H-indole |
| 1H-Indole, 5-fluoro- |
| 5-Fluoro-1H-indole |
| MFCD00056933 |
| 5-Fluoro indole |
| 6-FLUOROINDOLE FOR SYNTHESIS 5 G |
| 1H-INDOLE,6-FLUORO |
| 1H-Indole, 6-fluoro- |
| 5-Fluoroindole |
 CAS#:96631-90-2
CAS#:96631-90-2 CAS#:446-10-6
CAS#:446-10-6 CAS#:4637-24-5
CAS#:4637-24-5 CAS#:120192-70-3
CAS#:120192-70-3 CAS#:3093-97-8
CAS#:3093-97-8 CAS#:255724-68-6
CAS#:255724-68-6 CAS#:459-57-4
CAS#:459-57-4 CAS#:136818-43-4
CAS#:136818-43-4 CAS#:348-37-8
CAS#:348-37-8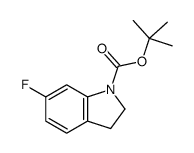 CAS#:1065183-64-3
CAS#:1065183-64-3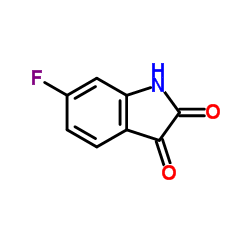 CAS#:324-03-8
CAS#:324-03-8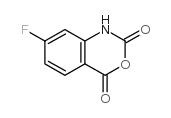 CAS#:321-50-6
CAS#:321-50-6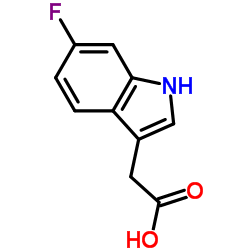 CAS#:443-75-4
CAS#:443-75-4 CAS#:225366-90-5
CAS#:225366-90-5 CAS#:343-93-1
CAS#:343-93-1 CAS#:2343-23-9
CAS#:2343-23-9 CAS#:255724-72-2
CAS#:255724-72-2 CAS#:1316695-35-8
CAS#:1316695-35-8 CAS#:1043601-53-1
CAS#:1043601-53-1
