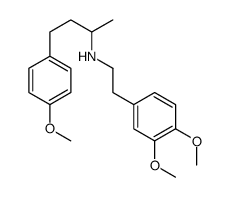
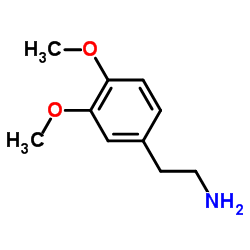
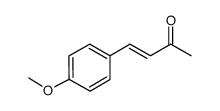
dobutamine
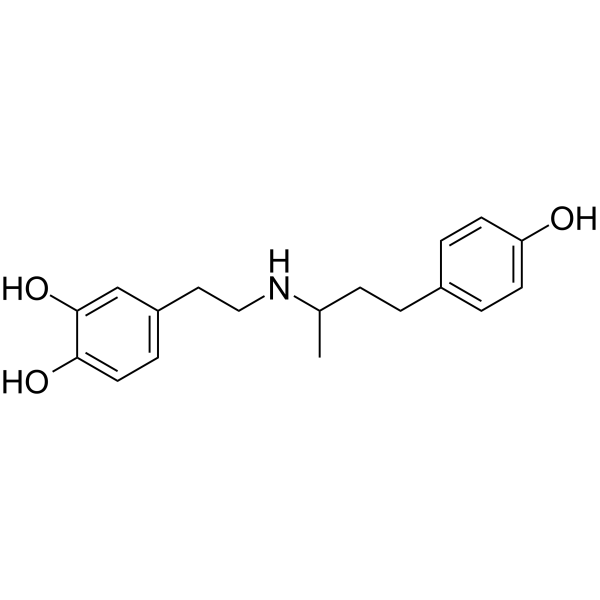
dobutamine structure
|
Common Name | dobutamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 34368-04-2 | Molecular Weight | 301.38000 | |
| Density | 1.189g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 527.7ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H23NO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 169.8ºC | |
Use of dobutamineDobutamine is a synthetic catecholamine that acts on α1-AR, β1-AR, β2-AR (α-1, β-1 andβ-2 adrenoceptors). Dobutamine is a selective β1-AR agonist, relatively weak activity at α1-AR and β2-AR. Dobutamine can increase cardiac output and correct hypoperfusion[1][2][3][4]. |
| Name | dobutamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dobutamine is a synthetic catecholamine that acts on α1-AR, β1-AR, β2-AR (α-1, β-1 andβ-2 adrenoceptors). Dobutamine is a selective β1-AR agonist, relatively weak activity at α1-AR and β2-AR. Dobutamine can increase cardiac output and correct hypoperfusion[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Dobutamine has a rapid onset of action and a short half-life [2]. Dobutamine (0.15-20 mg/kg; i.p.) results in subsequent increase in the left ventricular function and heart rate acceleration with an increasing dose in wildtype mice[3]. Dobutamine results in significant inotropic, lusitropic, and chronotropic cardiac response with a high dose in wildtype mice[3]. Low doses of Dobutamine significantly increases inotropic and lusitropic cardiac performance without chronotropic changes in the Tgαq*44 mice[3]. Dobutamine increases heart rate only after high doses, but then inotropic and lusitropic cardiac functional reserve is lost[3]. Dobutamine increases alveolar liquid clearance in ventilated rats by beta-2 receptor stimulation[4]. Animal Model: Tgαq*44 mice (heart failure models)[3] Dosage: 0.15 mg/kg, 0.5 mg/kg as a low dose, 1.5 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg as a high dose Administration: Intraperitoneal injection Result: Induced different response in cardiac function on a low and high dose in mice with with heart failure. |
| References |
| Density | 1.189g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 527.7ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H23NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 301.38000 |
| Flash Point | 169.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 301.16800 |
| PSA | 72.72000 |
| LogP | 3.34770 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | 20/21/22-63 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-26-36/37/39 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|
~92% 
dobutamine CAS#:34368-04-2 |
| Literature: SUN PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LIMITED Patent: WO2008/47382 A2, 2008 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 22 ; |
|
~% 
dobutamine CAS#:34368-04-2 |
| Literature: US3987200 A1, ; |
|
~% 
dobutamine CAS#:34368-04-2 |
| Literature: WO2008/47382 A2, ; Page/Page column 21 ; |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922509090. other amino-alcohol-phenols, amino-acid-phenols and other amino-compounds with oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
| 4-[2-[[3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-1-methylpropyl]amino]ethyl]-1,2-benzenediol |
| DOBUTAMINE HCL |
| 1,2-Benzenediol,4-[2-[[3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-methylpropyl]amino]ethyl]-,(+-) |
| (+/-)-dobutamine |
| DOBUTAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE |
| 4-[2-[4-(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)BUTAN-2-YLAMINO]ETHYL]BENZENE-1,2-DIOL |