Diclofensine (hydrochloride)
Modify Date: 2025-08-26 10:30:06
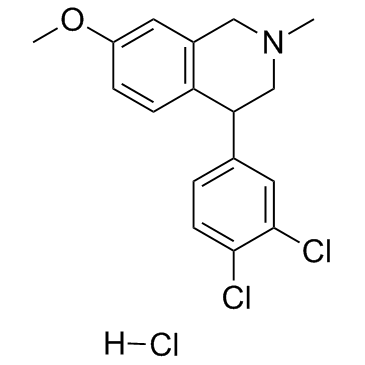
Diclofensine (hydrochloride) structure
|
Common Name | Diclofensine (hydrochloride) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 34041-84-4 | Molecular Weight | 358.690 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H18Cl3NO | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Diclofensine (hydrochloride)Diclofensine(Ro-8-4650) is a potent inhibitor of monoamine reuptake, blocking the uptake of dopamine, noradrenaline, and serotonin by rat brain synaptosomes with IC50 values of 0.74, 2.3, and 3.7 nM, respectively.IC50 value:Target: Dopamine reuptake inhibitorThe action of diclofensine on peripheral neuronal adrenergic function was studied through tests of the blood pressure response to NE, tyramine, and phenylephrine (PE). The blood pressure response to NE was enhanced and that to tyramine was decreased by diclofensine, as a result of its inhibitive action on peripheral neuronal amine uptake [2]. Diclofensine, in concentrations of 0.01, 0.1 and 1 microM caused a marked decrease of 3H-DA uptake. In addition, it was unable to stimulate basal endogenous DA release which, on the contrary, was elicited by d-amphetamine in the same concentration (50 microM). On the other hand, diclofensine (50 microM) caused a 3 fold enhancement of K+-evoked DA release [3]. |
| Name | Diclofensine Hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Diclofensine(Ro-8-4650) is a potent inhibitor of monoamine reuptake, blocking the uptake of dopamine, noradrenaline, and serotonin by rat brain synaptosomes with IC50 values of 0.74, 2.3, and 3.7 nM, respectively.IC50 value:Target: Dopamine reuptake inhibitorThe action of diclofensine on peripheral neuronal adrenergic function was studied through tests of the blood pressure response to NE, tyramine, and phenylephrine (PE). The blood pressure response to NE was enhanced and that to tyramine was decreased by diclofensine, as a result of its inhibitive action on peripheral neuronal amine uptake [2]. Diclofensine, in concentrations of 0.01, 0.1 and 1 microM caused a marked decrease of 3H-DA uptake. In addition, it was unable to stimulate basal endogenous DA release which, on the contrary, was elicited by d-amphetamine in the same concentration (50 microM). On the other hand, diclofensine (50 microM) caused a 3 fold enhancement of K+-evoked DA release [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C17H18Cl3NO |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 358.690 |
| Exact Mass | 357.045410 |
| PSA | 12.47000 |
| LogP | 5.31920 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Isoquinoline, 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-7-methoxy-2-methyl-, hydrochloride |
| 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-7-methoxy-2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Isoquinoline, 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-7-methoxy-2-methyl-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-7-methoxy-2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoqu inoline hydrochloride (1:1) |
| UNII:8U71XY6JQK |
| Diclofensine (hydrochloride) |