Oleuropein
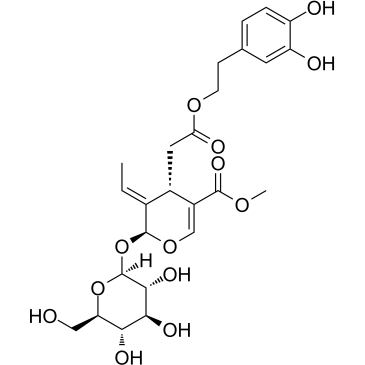
Oleuropein structure
|
Common Name | Oleuropein | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 32619-42-4 | Molecular Weight | 540.514 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 772.9±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H32O13 | Melting Point | 89-90ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 257.0±26.4 °C | |
Use of OleuropeinOleuropein, found in olive leaves and oil, exerts antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic effects through direct inhibition of PPARγ transcriptional activity[1]. Oleuropein induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells via the p53-dependent pathway and through the regulation of Bax and Bcl2 genes. Oleuropein also inhibits aromatase[2]. |
| Name | Oleuropein |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Oleuropein, found in olive leaves and oil, exerts antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic effects through direct inhibition of PPARγ transcriptional activity[1]. Oleuropein induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells via the p53-dependent pathway and through the regulation of Bax and Bcl2 genes. Oleuropein also inhibits aromatase[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PPARγ Apoptosis Aromatase |
| In Vitro | Aromatase, a cytochrome P450 enzyme, is an important pharmacological target in breast cancer therapy[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 772.9±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 89-90ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C25H32O13 |
| Molecular Weight | 540.514 |
| Flash Point | 257.0±26.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 540.184265 |
| PSA | 201.67000 |
| LogP | -0.91 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.630 |
| InChIKey | RFWGABANNQMHMZ-DXNYSGJVSA-N |
| SMILES | CC=C1C(OC2OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C2O)OC=C(C(=O)OC)C1CC(=O)OCCc1ccc(O)c(O)c1 |
| Storage condition | room temp |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2938909090 |
|---|
|
Rapid screening of oleuropein from olive leaves using matrix solid-phase dispersion and high-performance liquid chromatography.
J. AOAC Int. 97(4) , 1109-13, (2014) Matrix solid-phase dispersion (MSPD) methodology as a quick and easy extraction method has been developed to extract oleuropein from Olea europaea leaves. This method has been compared with convention... |
|
|
A metabolite-profiling approach to assess the uptake and metabolism of phenolic compounds from olive leaves in SKBR3 cells by HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 72 , 121-6, (2013) Olive leaves, an easily available natural low-cost material, constitute a source of extracts with significant antitumor activity that inhibits cell proliferation in several breast-cancer-cell models. ... |
|
|
Antiproliferative effect of oleuropein in prostate cell lines.
Int. J. Oncol. 41(1) , 31-8, (2012) Currently, there is increasing interest in the in vivo protective effects of natural antioxidants found in dietary plants against oxidative damage caused by free radical species. Oxidative stress has ... |
| Olive Leaf Extract |
| MFCD00017493 |
| Oleuropein |
| oleuropein glucoside |
| EINECS 251-129-6 |
| Methyl (2S,3E,4S)-4-{2-[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]-2-oxoethyl}-3-ethylidene-2-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-5-carboxylate |
| 2H-Pyran-4-acetic acid, 3-ethylidene-2-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3,4-dihydro-5-(methoxycarbonyl)-, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl ester, (2S,3E,4S)- |
 CAS#:10597-60-1
CAS#:10597-60-1 CAS#:178600-68-5
CAS#:178600-68-5
