Triflusal
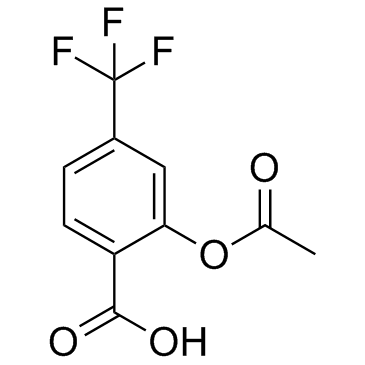
Triflusal structure
|
Common Name | Triflusal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 322-79-2 | Molecular Weight | 248.155 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 316.0±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H7F3O4 | Melting Point | 115 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 144.9±27.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of TriflusalTriflusal irreversibly inhibits the production of thromboxane-B2 in platelets by acetylating cycloxygenase-1.Target: COXTriflusal at 10 mM, 100 mM and 1 M decreases LDH efflux in rat brain slices after anoxia/reoxygenation by 24%, 35% and 49% respectively. Triflusal also reduces inducible NO synthase activity by 18%, 21% and 30% [1].Triflusal (10 mg/kg i.v.) reduces platelet deposition on subendothelium-induced primary thrombus by about 68% in rabbits. Triflusal (10 mg/kg i.v.) reduces platelet deposition on a fresh thrombus formed over tunica media by about 48% in rabbits. Triflusal (40 mg/kg p.o.) reduces platelet deposition on a primary thrombus triggered by subendothelium and tunica media by 53% in rabbits. Triflusal (40 mg/kg p.o.) significantly reduces Cox-2 mRNA levels and protein levels without influence Cox-1 mRNA levels on the vascular wall in rabbits [2]. Triflusal (600 mg/day for 5 days) results in an increase in NO production by neutrophils and an increase in endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) protein expression in neutrophils in healthy volunteers [3]. |
| Name | 2-acetyloxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Triflusal irreversibly inhibits the production of thromboxane-B2 in platelets by acetylating cycloxygenase-1.Target: COXTriflusal at 10 mM, 100 mM and 1 M decreases LDH efflux in rat brain slices after anoxia/reoxygenation by 24%, 35% and 49% respectively. Triflusal also reduces inducible NO synthase activity by 18%, 21% and 30% [1].Triflusal (10 mg/kg i.v.) reduces platelet deposition on subendothelium-induced primary thrombus by about 68% in rabbits. Triflusal (10 mg/kg i.v.) reduces platelet deposition on a fresh thrombus formed over tunica media by about 48% in rabbits. Triflusal (40 mg/kg p.o.) reduces platelet deposition on a primary thrombus triggered by subendothelium and tunica media by 53% in rabbits. Triflusal (40 mg/kg p.o.) significantly reduces Cox-2 mRNA levels and protein levels without influence Cox-1 mRNA levels on the vascular wall in rabbits [2]. Triflusal (600 mg/day for 5 days) results in an increase in NO production by neutrophils and an increase in endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) protein expression in neutrophils in healthy volunteers [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX-2:280 μM (IC50) COX-2:160 μM (IC50, in human blood) |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 316.0±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 115 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C10H7F3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 248.155 |
| Flash Point | 144.9±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 248.029648 |
| PSA | 63.60000 |
| LogP | 2.90 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.484 |
| InChIKey | RMWVZGDJPAKBDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=O)Oc1cc(C(F)(F)F)ccc1C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H317-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 22-36/37/38-43 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | GP4250000 |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
|
~% 
Triflusal CAS#:322-79-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 76, p. 1051,1054 |
|
~% 
Triflusal CAS#:322-79-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 76, p. 1051,1054 |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918990090. other carboxylic acids with additional oxygen function and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Long-term follow-up of atrial fibrillation patients in the NASPEAF study. Prospective evaluation of different antiplatelet treatments.
Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 62(9) , 992-1000, (2009) In the NASPEAF (National Study for Prevention of Embolism in Atrial Fibrillation) trial, combination therapy with an anticoagulant and an antiplatelet was more effective than anticoagulation alone in ... |
|
|
Electrochemical behavior of triflusal, aspirin and their metabolites at glassy carbon and boron doped diamond electrodes.
Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen 13(7) , 569-77, (2010) The electrochemical behavior of triflusal (TRF) and aspirin (ASA), before and after hydrolysis in water and in alkaline medium using two different electrode surfaces, glassy carbon and boron doped dia... |
|
|
A phase I study to characterize the multiple-dose pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of new enteric-coated triflusal formulations in healthy male volunteers.
Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 7(12) , 1471-9, (2011) An enteric-coated formulation of triflusal (triflusal EC), an antiplatelet agent, was developed to reduce the high incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events (AEs). The aim of this study is to compa... |
| Triflusal |
| 2-(acetyloxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid |
| α,α,α-Trifluoro-2,4-cresotic Acid Acetate |
| 2-Acetoxy-4-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid |
| EINECS 206-297-5 |
| Triflusalum [INN-Latin] |
| 2-Acetoxy-4-trifluoromethylbenzoicacid |
| Benzoic acid, 2-(acetyloxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)- |
| Triflusal [INN] |
| 2-Acetoxy-4-trifluormethyl-benzoesaeure |
| 2-Acetoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid |
| 2-Acetyloxy-4-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid |
| UR 1501 |
| MFCD00866793 |
| Disgren |
| Triflux |