STF-62247
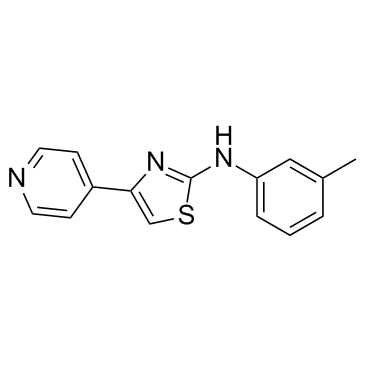
STF-62247 structure
|
Common Name | STF-62247 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 315702-99-9 | Molecular Weight | 267.349 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 444.8±47.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H13N3S | Melting Point | 174.66° C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 222.8±29.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of STF-62247STF-62247 is TGN inhibitor with IC50 of 0.625μM and 16μM in RCC4 and RCC4/VHL cells,respectively.It specifically induces autophagic cell death in cells that have lost VHL, an essential mutation in the development of RCC.IC50: 0.625/16μM in RCC4 and RCC4/VHL cells,respectively.[1]In vitro: STF-62247 induces cytotoxicity in VHL-deficient cells in a HIF-independent manner, STF-62247 increases acidification in VHL-deficient cells ,TGN is a target of STF-62247 and a drug-selective pathway synthetically lethal in VHL-deficient cells.[1] Golgi trafficking are required as initial signals in STF-62247-induced autophagy.[2]STF-62247 increases radiosensitivity in a VHL-dependent manner.[3]In vivo: SN12C, SN12C-VHL shRNA, or 786-O cells were implanted subcutaneously into the flanks of immunodeficient mice. The selective cytotoxicity of STF-62247 for the VHL-deficient cells was also demonstrated in 786-O cells compared to their wild-type VHL counterparts by clonogenic assay in vitro. Daily treatment with STF-62247 significantly reduced tumor growth of VHL-deficient cells. This decrease in tumor growth was concentration dependent. Importantly, drug treatment did not have any effect on the growth of SN12C tumor cells that have wild-type VHL. Together,STF-62247 reduces tumor growth in VHL-deficient cells in mice.[1] |
| Name | N-(3-methylphenyl)-4-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-thiazol-2-amine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | STF-62247 is TGN inhibitor with IC50 of 0.625μM and 16μM in RCC4 and RCC4/VHL cells,respectively.It specifically induces autophagic cell death in cells that have lost VHL, an essential mutation in the development of RCC.IC50: 0.625/16μM in RCC4 and RCC4/VHL cells,respectively.[1]In vitro: STF-62247 induces cytotoxicity in VHL-deficient cells in a HIF-independent manner, STF-62247 increases acidification in VHL-deficient cells ,TGN is a target of STF-62247 and a drug-selective pathway synthetically lethal in VHL-deficient cells.[1] Golgi trafficking are required as initial signals in STF-62247-induced autophagy.[2]STF-62247 increases radiosensitivity in a VHL-dependent manner.[3]In vivo: SN12C, SN12C-VHL shRNA, or 786-O cells were implanted subcutaneously into the flanks of immunodeficient mice. The selective cytotoxicity of STF-62247 for the VHL-deficient cells was also demonstrated in 786-O cells compared to their wild-type VHL counterparts by clonogenic assay in vitro. Daily treatment with STF-62247 significantly reduced tumor growth of VHL-deficient cells. This decrease in tumor growth was concentration dependent. Importantly, drug treatment did not have any effect on the growth of SN12C tumor cells that have wild-type VHL. Together,STF-62247 reduces tumor growth in VHL-deficient cells in mice.[1] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 444.8±47.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 174.66° C |
| Molecular Formula | C15H13N3S |
| Molecular Weight | 267.349 |
| Flash Point | 222.8±29.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 267.083008 |
| PSA | 66.05000 |
| LogP | 3.16 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.671 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~87% 
STF-62247 CAS#:315702-99-9 |
| Literature: Hay, Michael P.; Turcotte, Sandra; Flanagan, Jack U.; Bonnet, Muriel; Chan, Denise A.; Sutphin, Patrick D.; Nguyen, Phuong; Giaccia, Amato J.; Denny, William A. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2010 , vol. 53, # 2 p. 787 - 797 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Novel small-molecule SIRT1 inhibitors induce cell death in adult T-cell leukaemia cells.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 11345, (2015) Adult T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma (ATL) is an aggressive T-cell malignancy that develops after long-term infection with human T-cell leukaemia virus (HTLV)-1. The identification of new molecular targets... |
|
|
Targeted therapy for the loss of von Hippel-Lindau in renal cell carcinoma: a novel molecule that induces autophagic cell death.
Autophagy 4(7) , 944-6, (2008) Radiation and conventional cytotoxic chemotherapies are ineffective in treating renal cancer. Approximately 75 percent of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is associated with an inactivation of the tumor sup... |
|
|
A novel method for autophagy detection in primary cells: impaired levels of macroautophagy in immunosenescent T cells.
Autophagy 8 , 677-89, (2012) Autophagy is a conserved constitutive cellular process, responsible for the degradation of dysfunctional proteins and organelles. Autophagy plays a role in many diseases such as neurodegeneration and ... |
| STF-62247 |
| 2-Thiazolamine, N-(3-methylphenyl)-4-(4-pyridinyl)- |
| N-(3-Methylphenyl)-4-(4-pyridinyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-amine |
| N-(3-methyl-phenyl)-4-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-thiazol-2-amine |
| 4-(pyridin-4-yl)-N-m-tolylthiazol-2-amine |
| N-(3-Methylphenyl)-4-(4-pyridinyl)-2-thiazolamine |
| S1041_Selleck |