Azulene

Azulene structure
|
Common Name | Azulene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 275-51-4 | Molecular Weight | 128.171 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 220.7±7.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8 | Melting Point | 98-100 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 76.7±8.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS09 |
Signal Word | ||
Use of AzuleneAzulene (Cyclopentacycloheptene) is as an isomer of naphthalene with high anti-HIV activity. Azulene, isolated from the distillation of chamomile oil, is a scaffold in medicinal chemistry[1][2][3]. |
| Name | azulene |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Azulene (Cyclopentacycloheptene) is as an isomer of naphthalene with high anti-HIV activity. Azulene, isolated from the distillation of chamomile oil, is a scaffold in medicinal chemistry[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
HIV |
| In Vitro | Azulene is an interesting scaffold in medicinal chemistry as it resembles several other bicyclic aromatics that are frequently found in drugs. Azulene, a structural isomer of naphthalene, is a bicyclic nonbenzenoid aromatic hydrocarbon having a dipole moment due to the electron-rich five-membered ring and electron-deficient sevenmembered ring[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 220.7±7.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 98-100 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8 |
| Molecular Weight | 128.171 |
| Flash Point | 76.7±8.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 128.062607 |
| LogP | 3.45 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.2±0.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.632 |
| InChIKey | CUFNKYGDVFVPHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | c1ccc2cccc-2cc1 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2902909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2902909090 other aromatic hydrocarbons。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:2.0%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Determination of descriptors for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and related compounds by chromatographic methods and liquid-liquid partition in totally organic biphasic systems.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1361 , 240-54, (2014) Retention factors on several columns and at various temperatures using gas chromatography and from reversed-phase liquid chromatography on a SunFire C18 column with various mobile phase compositions c... |
|
|
Novel azulene-based derivatives as potent multi-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20(20) , 6129-32, (2010) A series of azulene-based derivatives were synthesized as potent inhibitors for receptor tyrosine kinases such as FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT-3). Systematic side chain modification of prototype 1a... |
|
|
Total synthesis of a CD-ring: side-chain building block for preparing 17-epi-calcitriol derivatives from the Hajos-Parrish dione.
J. Org. Chem. 76(16) , 6906-11, (2011) An efficient synthesis of the key building block for 17-epi-calctriol from the Hajos-Parrish dione involving a sequence of diastereoselective transformation of the azulene core and the side-chain cons... |
| Bicyclo[5.3.0]deca-2,4,6,8,10-pentaene |
| EINECS 205-993-6 |
| Cyclopentacycloheptene |
| Azunol |
| Bicyclo(5.3.0)-deca-2,4,6,8,10-pentaene |
| MFCD00003810 |
| Azulene |
| Bicyclo(5.3.0)-1,3,5,7,9-decapentaene |
| Bicyclo[5.3.0]decapentaene |
| Bicyclo[0.3.5]deca-1,3,5,7,9-pentaene |
| Azunamic |
 CAS#:23306-02-7
CAS#:23306-02-7 CAS#:36044-41-4
CAS#:36044-41-4 CAS#:36044-31-2
CAS#:36044-31-2 CAS#:607393-61-3
CAS#:607393-61-3 CAS#:52487-41-9
CAS#:52487-41-9 CAS#:90266-03-8
CAS#:90266-03-8 CAS#:84176-25-0
CAS#:84176-25-0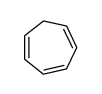 CAS#:544-25-2
CAS#:544-25-2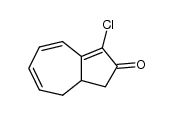 CAS#:393091-18-4
CAS#:393091-18-4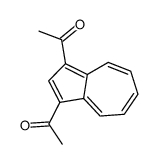 CAS#:10487-55-5
CAS#:10487-55-5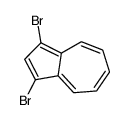 CAS#:14658-95-8
CAS#:14658-95-8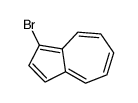 CAS#:61035-76-5
CAS#:61035-76-5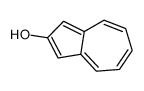 CAS#:19384-00-0
CAS#:19384-00-0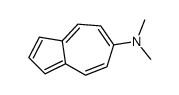 CAS#:2048-68-2
CAS#:2048-68-2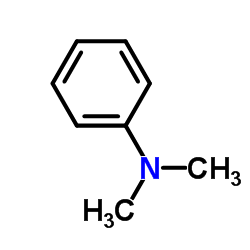 CAS#:121-69-7
CAS#:121-69-7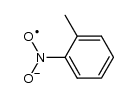 CAS#:34505-30-1
CAS#:34505-30-1 CAS#:35963-33-8
CAS#:35963-33-8 CAS#:460-12-8
CAS#:460-12-8
