Eribulin
Modify Date: 2025-08-21 10:59:12
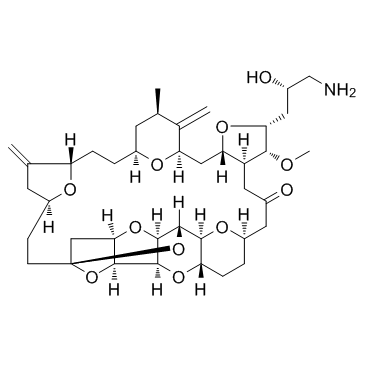
Eribulin structure
|
Common Name | Eribulin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 253128-41-5 | Molecular Weight | 729.897 | |
| Density | 1.29±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C40H59NO11 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of EribulinEribulin (E7389; ER-086526), a synthetic analogue of halichondrin B in phase III clinical trials for breast cancer, binds to tubulin and microtubules.Target: Microtubule/TubulinEribulin suppressed centromere dynamics at concentrations that arrest mitosis. At 60 nmol/L eribulin (2 x mitotic IC(50)), the relaxation rate was suppressed 21%, the time spent paused increased 67%, and dynamicity decreased 35% (but without reduction in mean centromere separation), indicating that eribulin decreased normal microtubule-dependent spindle tension at the kinetochores, preventing the signal for mitotic checkpoint passage [1]. [(3)H]eribulin binds soluble tubulin at a single site; however, this binding is complex with an overall K(d) of 46 microM, but also showing a real or apparent very high affinity (K(d) = 0.4 microM) for a subset of 25% of the tubulin. Eribulin also binds microtubules with a maximum stoichiometry of 14.7 +/- 1.3 molecules per microtubule (K(d) = 3.5 microM), strongly suggesting the presence of a relatively high-affinity binding site at microtubule ends. At 100 nM, the concentration that inhibits microtubule plus end growth by 50%, we found that one molecule of eribulin is bound per two microtubules, indicating that the binding of a single eribulin molecule at a microtubule end can potently inhibit its growth. Eribulin does not suppress dynamic instability at microtubule minus ends [2]. Eribulin's in vivo superiority derives from its ability to induce irreversible mitotic blockade, which appears related to persistent drug retention and sustained Bcl-2 phosphorylation [3]. |
| Name | eribulin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Eribulin (E7389; ER-086526), a synthetic analogue of halichondrin B in phase III clinical trials for breast cancer, binds to tubulin and microtubules.Target: Microtubule/TubulinEribulin suppressed centromere dynamics at concentrations that arrest mitosis. At 60 nmol/L eribulin (2 x mitotic IC(50)), the relaxation rate was suppressed 21%, the time spent paused increased 67%, and dynamicity decreased 35% (but without reduction in mean centromere separation), indicating that eribulin decreased normal microtubule-dependent spindle tension at the kinetochores, preventing the signal for mitotic checkpoint passage [1]. [(3)H]eribulin binds soluble tubulin at a single site; however, this binding is complex with an overall K(d) of 46 microM, but also showing a real or apparent very high affinity (K(d) = 0.4 microM) for a subset of 25% of the tubulin. Eribulin also binds microtubules with a maximum stoichiometry of 14.7 +/- 1.3 molecules per microtubule (K(d) = 3.5 microM), strongly suggesting the presence of a relatively high-affinity binding site at microtubule ends. At 100 nM, the concentration that inhibits microtubule plus end growth by 50%, we found that one molecule of eribulin is bound per two microtubules, indicating that the binding of a single eribulin molecule at a microtubule end can potently inhibit its growth. Eribulin does not suppress dynamic instability at microtubule minus ends [2]. Eribulin's in vivo superiority derives from its ability to induce irreversible mitotic blockade, which appears related to persistent drug retention and sustained Bcl-2 phosphorylation [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.29±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C40H59NO11 |
| Molecular Weight | 729.897 |
| Exact Mass | 729.408813 |
| PSA | 146.39000 |
| LogP | 3.88 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.584 |
| InChIKey | UFNVPOGXISZXJD-JBQZKEIOSA-N |
| SMILES | C=C1CC2CCC34CC5OC6C(OC7CCC(CC(=O)CC8C(CC9OC(CCC1O2)CC(C)C9=C)OC(CC(O)CN)C8OC)OC7C6O3)C5O4 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Water Solubility | Practically insoluble (0.015 g/L) (25 ºC) |
| Cyclopentanecarboxylicacid,3-[[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]amino]-4-hydroxy-,methyl ester,(1S,3S,4R) |
| Eribulin |
| (1S,3S,4R)-3-tert-butoxycarbonylamino-4-hydroxycyclopentanecarboxylic acid methyl ester |
| 2-(3-Amino-2-hydroxypropyl)hexacosahydro-3-methoxy- 26-methyl-20,27-bis(methylene)11,15-18,21-24,28-triepoxy- 7,9-ethano-12,15-methano-9H,15H-furo(3,2-i)furo(2',3'-5,6) pyrano(4,3-b)(1,4)dioxacyclopentacosin-5-(4H)-one |
| NSC-707389 |
| Methyl(1S,3S,4R)NBOC3amino4hydroxycyclopentanecarboxylate |
| Halaven |
| (1S,3S,6S,9S,12S,14R,16R,18S,20R,21R,22S,26R,29S,31R,32S,33S,35R,36S)-20-[(2S)-3-Amino-2-hydroxypropyl]-21-methoxy-14-methyl-8,15-bis(methylene)-2,19,30,34,37,39,40,41-octaoxanonacyclo[24.9.2.1. 1.1.1.0.0.0]hentetracontan-24-one |
| ER-086526 |
| (1S,3S,6S,9S,12S,14R,16R,18S,20R,21R,22S,26R,29S,31R,32S,33R,35R,36S)-20-[(2S)-3-Amino-2-hydroxypropyl]-21-methoxy-14-methyl-8,15-bis(methylene)-2,19,30,34,37,39,40,41-octaoxanonacyclo [24.9.2.13,32.13,33.16,9.112,16.018,22.029,36.031,35]hentetracontan-24-one |