Chebulagic acid
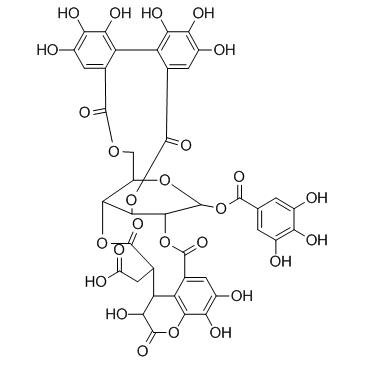
Chebulagic acid structure
|
Common Name | Chebulagic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23094-71-5 | Molecular Weight | 954.661 | |
| Density | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1610.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C41H30O27 | Melting Point | >300℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 480.0±27.8 °C | |
Use of Chebulagic acidChebulagic acid is a COX-LOX dual inhibitor isolated from the fruits of Terminalia chebula Retz, on angiogenesis.target: COX-LOX [1]In vitro: Chebulagic acid can enhance the autophagy. Chebulagic acid exert anti-inflammatory and anti-infective effects. [1] [2] Chebulagic acid also show a protective effect against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) - induce cytotoxicity which mimics the pathological symptom of Parkinson's disease. Chebulagic acid inhibit the LPS-induced upregulation of TNF-α and IL-1β in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Furthermore, LPS-activated MAPK signaling is inhibited by CA treatment in the EA.hy926 cells. [3] |
| Name | 1-O-galloyl-2,4-O-chebuloyl-3,6-O-HHDP-β-D-glucose |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Chebulagic acid is a COX-LOX dual inhibitor isolated from the fruits of Terminalia chebula Retz, on angiogenesis.target: COX-LOX [1]In vitro: Chebulagic acid can enhance the autophagy. Chebulagic acid exert anti-inflammatory and anti-infective effects. [1] [2] Chebulagic acid also show a protective effect against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) - induce cytotoxicity which mimics the pathological symptom of Parkinson's disease. Chebulagic acid inhibit the LPS-induced upregulation of TNF-α and IL-1β in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Furthermore, LPS-activated MAPK signaling is inhibited by CA treatment in the EA.hy926 cells. [3] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1610.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C41H30O27 |
| Molecular Weight | 954.661 |
| Flash Point | 480.0±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 954.097473 |
| PSA | 447.09000 |
| LogP | 2.25 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.876 |
| InChIKey | HGJXAVROWQLCTP-JGPATRSISA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CC1C(=O)OC2C3COC(=O)c4cc(O)c(O)c(O)c4-c4c(cc(O)c(O)c4O)C(=O)OC2C(OC(=O)c2cc(O)c(O)c4c2C1C(O)C(=O)O4)C(OC(=O)c1cc(O)c(O)c(O)c1)O3 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
|
Chemical changes during fermentation of Abhayarishta and its standardization by HPLC-DAD.
Nat. Prod. Commun. 5(4) , 575-9, (2010) Abhayarishta is an Ayurvedic formulation prepared traditionally by the fermentation of the decoction of Terminalia chebula (pericarp), Vitis vinifera (fruits), Embelia ribes (fruits) and Madhuca indic... |
|
|
[Analysis of tannins in Fructus Chebulae and its confusion varieties by HPCE].
Yao Xue Xue Bao 36(4) , 292-5, (2001) To analyze the hydrolyzable tannins-chebulinic acid (I) and chebulagic acid(II) in Fructus Chebulae and its confusion varieties by using high performance capillary electrophoresis (HPCE) method.Using ... |
|
|
[Assay of three hydrolyzable tannins in Fructus Chebulae from different habitats by RP-HPLC].
Zhong Yao Cai 23(6) , 328-30, (2000) Three hydrolyzable tannins chebulinic acid (I), chebulagic acid(II) and 1,3, 6-tri-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose (III) in Fructus Chebulae from different habitats were determined by RP-HPLC method. The con... |
| Chebulagic acid |
| [(4R,5S,7R,25S,26R,29S,30S,31S)-13,14,15,18,19,20,31,35,36-Nonahydroxy-2,10,23,28,32-pentaoxo-5-[(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy]-3,6,9,24,27,33-hexaoxaheptacyclo[28.7.1.0.0.0.0 .0]octatriaconta-1(38),11,13,15,17,19,21,34,36-nonaen-29-yl]acetic acid |
| 10,24-(Epoxymethano)-11H-4,9,12,23,25-pentaoxadibenzo[5',6':7',8']cyclododeca[1',2':7,8]cycloundeca[1,2,3-de]naphthalene-7-acetic acid, 5,6,6a,7,8,9a,10,13,22,23a,24,26-dodecahydro-2,3,6,15,16,17,18,19,20-nonahydroxy-5,8,13,22,26-pentaoxo-27-[(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy]-, (6S,6aS,7S,9aR,10R,23aS,24R,27S)- |
| CHEBULAGIC ACID(RG) |
 CAS#:1707-75-1
CAS#:1707-75-1
