DL-TBOA ammonium
Modify Date: 2025-08-26 21:57:14
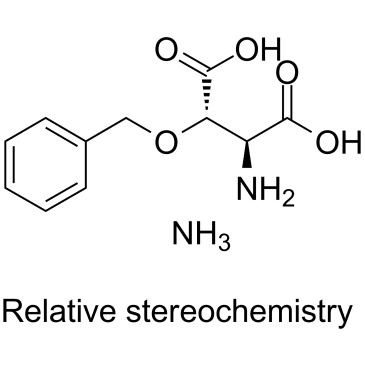
DL-TBOA ammonium structure
|
Common Name | DL-TBOA ammonium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2093503-71-8 | Molecular Weight | 256.26 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H16N2O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of DL-TBOA ammoniumDL-TBOA ammonium is a potent non-transportable inhibitor of excitatory amino acid transporters with IC50s of 70 μM, 6 μM and 6 μM for excitatory amino acid transporter-1 (EAAT1), EAAT2 and EAAT3, respectively. DL-TBOA ammonium inhibits the uptake of [14C]glutamate in COS-1 cells expressing the human EAAT1 and EAAT2 with Ki valuesof 42 μM and 5.7 μM, respectively. DL-TBOA ammonium blocks EAAT4 and EAAT5 in a competitive manner with Ki values of 4.4 μM and 3.2 μM, respectively[1][2][3]. |
| Name | DL-TBOA ammonium |
|---|
| Description | DL-TBOA ammonium is a potent non-transportable inhibitor of excitatory amino acid transporters with IC50s of 70 μM, 6 μM and 6 μM for excitatory amino acid transporter-1 (EAAT1), EAAT2 and EAAT3, respectively. DL-TBOA ammonium inhibits the uptake of [14C]glutamate in COS-1 cells expressing the human EAAT1 and EAAT2 with Ki valuesof 42 μM and 5.7 μM, respectively. DL-TBOA ammonium blocks EAAT4 and EAAT5 in a competitive manner with Ki values of 4.4 μM and 3.2 μM, respectively[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 70 μM (EAAT1), 6 μM (EAAT2) and 6 μM (EAAT3); Ki: 42 μM (human EAAT1), 5.7 μM (human EAAT2), 4.4 μM (EAAT4) and 3.2 μM (EAAT5)[1][2][3] |
| In Vitro | DL-TBOA ammonium (70-350 μM; 48 hours) treatment concentration-dependently enhances SN38-induced loss of viability. DL-TBOA reversed Oxaliplatin-induced loss of viability[4]. DL-TBOA ammonium (350 μM; 24 hours) decreases p53 induction by SN38 and oxaliplatin[4]. Cell Viability Assay[4] Cell Line: HCT116 cells, LoVo cells Concentration: 70 μM, 350 μM Incubation Time: 48 hours Result: Enhanced SN38-induced, and counteracted Oxaliplatin-induced, cell death. Cell Viability Assay[4] Cell Line: HCT116 cells, LoVo cells Concentration: 350 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: p53 induction by SN38 and oxaliplatin was decreased. |
| In Vivo | DL-TBOA ammonium (10 nmol; i.c.v.) to morphine-dependent rats significantly facilitates the expression of naloxone-precipitated somatic signs and conditioned place aversion[5]. Animal Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (180-250 g)[5] Dosage: 1 nmol, 3 nmol, 10 nmol Administration: Intracerebroventricularly injection (i.c.v.) Result: Dose dependently facilitated various somatic signs induced by Naloxone (0.1 mg/kg)-precipitated morphine withdrawal. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C11H16N2O5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 256.26 |