Solamargine
Modify Date: 2025-08-23 14:28:04
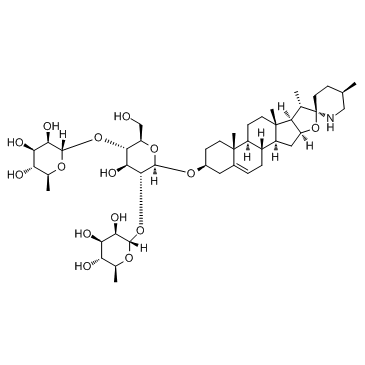
Solamargine structure
|
Common Name | Solamargine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 20311-51-7 | Molecular Weight | 868.059 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C45H73NO15 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of SolamargineSolamargine is a major steroidal alkaloid glycoside extracted from a traditional Chinese medicinal herb, Solanum nigrum L. (SNL); has been shown to inhibit growth and induce apoptosis of various cancer cells. IC50 value:Target: Anticancer natural compoundin vitro: Solamargine reduced HepG2 cell viability in a concentration-dependent manner. At 7.5μM solamargine decreased cell viability by less than 20% in HepG2 cells. At the highest dose, solamargine decreased cell migration and invasion by more than 70% and 72% in HepG2 cells, respectively. Western blotting and gelatin zymography results showed that solamargine reduced expression and function of MMP-2 and MMP-9 proteins [1]. SM increased phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) in a time-dependent fashion. SM also inhibited phosphorylation and protein expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3), a transcription factor, which was abrogated by the SB203580, a specific inhibitor of p38 MAPK. In addition, SM induced protein expression of p21, one of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, and this was not observed in cell overexpression of Stat3 or cells treated with SB203580 [2]. SM significantly inhibited the growth of SMMC-7721 and HepG2 cells and induced cell apoptosis. Cell cycle analysis revealed that SM caused cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. Moreover, SM could up-regulate the expression of caspase-3 [3]. |
| Name | Solamargine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Solamargine is a major steroidal alkaloid glycoside extracted from a traditional Chinese medicinal herb, Solanum nigrum L. (SNL); has been shown to inhibit growth and induce apoptosis of various cancer cells. IC50 value:Target: Anticancer natural compoundin vitro: Solamargine reduced HepG2 cell viability in a concentration-dependent manner. At 7.5μM solamargine decreased cell viability by less than 20% in HepG2 cells. At the highest dose, solamargine decreased cell migration and invasion by more than 70% and 72% in HepG2 cells, respectively. Western blotting and gelatin zymography results showed that solamargine reduced expression and function of MMP-2 and MMP-9 proteins [1]. SM increased phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) in a time-dependent fashion. SM also inhibited phosphorylation and protein expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3), a transcription factor, which was abrogated by the SB203580, a specific inhibitor of p38 MAPK. In addition, SM induced protein expression of p21, one of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, and this was not observed in cell overexpression of Stat3 or cells treated with SB203580 [2]. SM significantly inhibited the growth of SMMC-7721 and HepG2 cells and induced cell apoptosis. Cell cycle analysis revealed that SM caused cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. Moreover, SM could up-regulate the expression of caspase-3 [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C45H73NO15 |
| Molecular Weight | 868.059 |
| Exact Mass | 867.498047 |
| PSA | 238.48000 |
| LogP | 7.18 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.619 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| SOLAMERGINE |
| Solamargine |
| Solamargin |
| (3β,22α,25R)-Spirosol-5-en-3-yl 6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl-(1->2)-[6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl-(1->4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| β-D-Glucopyranoside, (3β,22α,25R)-spirosol-5-en-3-yl O-6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl-(1->2)-O-[6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl-(1->4)]- |
 CAS#:126-17-0
CAS#:126-17-0
