Benzo[e]pyrene
![Benzo[e]pyrene Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/142/192-97-2.png)
Benzo[e]pyrene structure
|
Common Name | Benzo[e]pyrene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 192-97-2 | Molecular Weight | 252.309 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 467.5±12.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H12 | Melting Point | 177-180ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 228.6±13.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Benzo[e]pyreneBenzo[e]pyrene occurs in fossil fuels and is a highly toxic member of a family of compounds called polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)[1]. |
| Name | benzo[e]pyrene |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Benzo[e]pyrene occurs in fossil fuels and is a highly toxic member of a family of compounds called polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 467.5±12.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 177-180ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C20H12 |
| Molecular Weight | 252.309 |
| Flash Point | 228.6±13.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 252.093903 |
| LogP | 6.40 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.887 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H350-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P273-P308 + P313-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T,N,Xn,F |
| Risk Phrases | 45-50/53-67-65-38-11 |
| Safety Phrases | S45;S53;S60;S61;S36/S37/S39 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DJ4200000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
|
Detection of benz[j]aceanthrylene in urban air and evaluation of its genotoxic potential.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 49(5) , 3101-9, (2015) Benz[j]aceanthrylene (B[j]A) is a cyclopenta-fused polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with strong mutagenic and carcinogenic effects. We have identified B[j]A in air particulate matter (PM) in samples co... |
|
|
Potential of goat probiotic to bind mutagens.
Anaerobe 28 , 8-12, (2014) The mutagen binding ability of the goat probiotics (Lactobacillus reuteri DDL 19, Lactobacillus alimentarius DDL 48, Enterococcus faecium DDE 39, and Bifidobacterium bifidum DDBA) was evaluated. The o... |
|
|
Exposure to dust-bound PAHs and associated carcinogenic risk in primitive and traditional cooking practices in Pakistan.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22 , 12644-54, (2015) The aim of this study was to determine the abundance and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in dust samples collected from the selected professional cooking workplaces (WCs) and r... |
| 4,5-Benzopyrene |
| 1,2-Benzpyrene,4,5-Benzpyrene |
| EINECS 205-892-7 |
| Benzo[l]pyrene |
| MFCD00003605 |
| 9,10-Benzpyrene |
| Benzo(a)pyrene |
| benzo<e>pyrene |
| Benzo(l)pyrene |
| Benzo(e)pyrene |
| Benzo[e]pyrene |
| B(e)P |
| 4,5-BENZPYRENE |
| benz[e]pyrene |
| 1,2-Benzopyrene |
| 1,2-Benzpyrene |
![9-Hydroxy-1,2,3,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-decahydrobenzo[e]pyrene Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/369/68151-09-7.png) CAS#:68151-09-7
CAS#:68151-09-7 CAS#:86439-17-0
CAS#:86439-17-0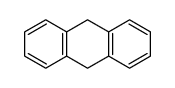 CAS#:613-31-0
CAS#:613-31-0 CAS#:107-02-8
CAS#:107-02-8 CAS#:77320-76-4
CAS#:77320-76-4![exo-4,5-dihydrobenzo[e]pyreno-2',3':4,5-norbornane Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/096/121617-90-1.png) CAS#:121617-90-1
CAS#:121617-90-1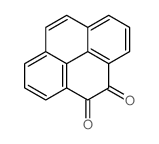 CAS#:6217-22-7
CAS#:6217-22-7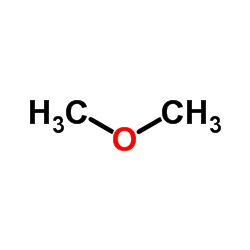 CAS#:115-10-6
CAS#:115-10-6![benzo[l]pyren-8-ol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/263/77508-25-9.png) CAS#:77508-25-9
CAS#:77508-25-9![1,2,3,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-DECAHYDROBENZ[E]PYRENE structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/369/92387-50-3.png) CAS#:92387-50-3
CAS#:92387-50-3
