3,6-DIOXA-1,8-OCTANEDITHIOL
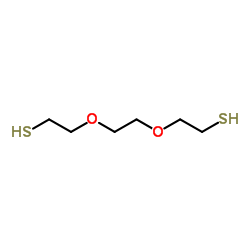
3,6-DIOXA-1,8-OCTANEDITHIOL structure
|
Common Name | 3,6-DIOXA-1,8-OCTANEDITHIOL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 14970-87-7 | Molecular Weight | 182.304 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 257.0±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H14O2S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 109.2±24.6 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | 2,2′-(Ethylenedioxy)diethanethiol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 257.0±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C6H14O2S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 182.304 |
| Flash Point | 109.2±24.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 182.043518 |
| PSA | 96.06000 |
| LogP | 0.95 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.495 |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H332-H411 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2810 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|
~% 
3,6-DIOXA-1,8-O... CAS#:14970-87-7 |
| Literature: Journal of Chemical Research, Miniprint, , # 1 p. 101 - 132 |
|
~92% 
3,6-DIOXA-1,8-O... CAS#:14970-87-7 |
| Literature: Synthesis, , # 4 p. 509 - 512 |
|
~55% 
3,6-DIOXA-1,8-O... CAS#:14970-87-7 |
| Literature: Synthesis, , # 3 p. 307 - 311 |
|
~63% 
3,6-DIOXA-1,8-O... CAS#:14970-87-7 |
| Literature: Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds, , vol. 38, # 4 p. 456 - 465 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
The influence of linker length on the properties of cathepsin S cleavable177Lu-labeled HPMA copolymers for pancreatic cancer imaging
Biomaterials 35(22) , 5760-70, (2014) N-(2-hydroxypropyl)-methacrylamide (HPMA) copolymers have shown promise for application in the detection and staging of cancer. However, non-target accumulation, particularly in the liver and spleen, ... |
|
|
Dual-targeted polyplexes based on sequence-defined peptide-PEG-oligoamino amides.
J. Pharm. Sci. 104(2) , 464-75, (2015) For active cell targeting, viruses frequently capitalize on dual-receptor binding. With the intention to mimic this natural process, a dual peptide-based approach for targeting cancer cells was evalua... |
|
|
Development and in vitro assessment of enzymatically-responsive poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels for the delivery of therapeutic peptides.
Biomaterials 35(36) , 9719-30, (2014) Despite the recent expansion of peptide drugs, delivery remains a challenge due to poor localization and rapid clearance. Therefore, a hydrogel-based platform technology was developed to control and s... |
| Ethanethiol, 2,2'-(1,2-ethanediylbis(oxy))bis- |
| Ethanethiol, 2,2'-[1,2-ethanediylbis(oxy)]bis- |
| 1,2-Bis(2-mercaptoethoxy)ethane,3,6-Dioxa-1,8-octane-dithiol |
| 2,2'-[1,2-Ethanediylbis(oxy)]diethanethiol |
| 3,6-DIOXA-1,8-OCTANEDITHIOL |
| 2-[2-(2-sulfanylethoxy)ethoxy]ethanethiol |
| 2,2'-(1,2-Ethanediylbis(oxy))bis(ethanethiol) |
| MFCD00015873 |
| 2,2'-[Ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy)]diethanethiol |
| 2,2'-(Ethylenedioxy)diethanethiol |
| EINECS 239-044-2 |
| 1,2-Bis(2-mercaptoethoxy)ethane |
| Ethylene Glycol Bis(2-mercaptoethyl) Ether |
| 1,8-Dimercapto-3,6-dioxaoctane |

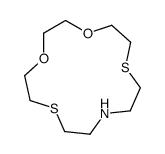 CAS#:150602-89-4
CAS#:150602-89-4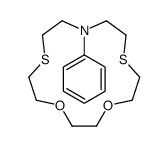 CAS#:240797-81-3
CAS#:240797-81-3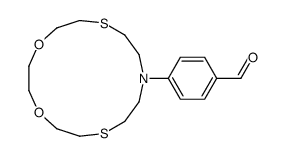 CAS#:240797-82-4
CAS#:240797-82-4 CAS#:40254-01-1
CAS#:40254-01-1
