Urea-d4
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 11:11:51
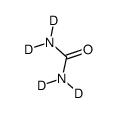
Urea-d4 structure
|
Common Name | Urea-d4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1433-11-0 | Molecular Weight | 64.07990 | |
| Density | 1.212g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 196.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | CD4N2O | Melting Point | 132-135ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 72.7ºC | |
Use of Urea-d4Urea-d4 is the deuterium labeled Urea[1]. Urea is a powerful protein denaturant via both direct and indirect mechanisms[2]. A potent emollient and keratolytic agent[3]. Used as a diuretic agent. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) has been utilized to evaluate renal function[4]. Widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen and is an important raw material for the chemical industry. |
| Name | 1,1,3,3-tetradeuteriourea |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Urea-d4 is the deuterium labeled Urea[1]. Urea is a powerful protein denaturant via both direct and indirect mechanisms[2]. A potent emollient and keratolytic agent[3]. Used as a diuretic agent. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) has been utilized to evaluate renal function[4]. Widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen and is an important raw material for the chemical industry. |
|---|---|
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.212g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 196.6ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 132-135ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | CD4N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 64.07990 |
| Flash Point | 72.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 64.05750 |
| PSA | 69.11000 |
| LogP | 0.42440 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.395mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.468 |
| InChIKey | XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-JBISRTOLSA-N |
| SMILES | NC(N)=O |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R40;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Differential stability of the bovine prion protein upon urea unfolding.
Protein Sci. 18(10) , 2172-82, (2009) Prion diseases, or transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, are a group of infectious neurological diseases associated with the structural conversion of an endogenous protein (PrP) in the central ne... |
| Urea-d4 |
| deuterourea |
| tetradeuteriourea |
| deuterated urea |
| EINECS 215-857-8 |
| MFCD00044227 |
| Tetradeuterio-harnstoff |