H-PRO-PHE-OH

H-PRO-PHE-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-PRO-PHE-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13589-02-1 | Molecular Weight | 262.30 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 531.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H18N2O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 275.5±30.1 °C | |
Use of H-PRO-PHE-OHH-Pro-Phe-OH is a dipeptide containing proline and phenylalanine, which can serve as a substrate for prolinase. H-Pro-Phe-OH can also be used for polypeptide synthesis, where phenylalanine is an aromatic amino acid that can inhibit the activity of Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE, HY-P2983)[1][2]. |
| Name | h-pro-phe-oh |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | H-Pro-Phe-OH is a dipeptide containing proline and phenylalanine, which can serve as a substrate for prolinase. H-Pro-Phe-OH can also be used for polypeptide synthesis, where phenylalanine is an aromatic amino acid that can inhibit the activity of Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE, HY-P2983)[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 531.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C14H18N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 262.30 |
| Flash Point | 275.5±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 262.131744 |
| PSA | 78.43000 |
| LogP | 0.67 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.568 |
|
~% 
H-PRO-PHE-OH CAS#:13589-02-1 |
| Literature: Freund, Matthias H.; Tsogoeva, Svetlana B. Synlett, 2011 , # 4 p. 503 - 507 |
|
~% 
H-PRO-PHE-OH CAS#:13589-02-1 |
| Literature: Gautschi, Markus; Schmid, Joachim P.; Peppard, Terry L.; Ryan, Thomas P.; Tuorto, Raymond M.; Yang, Xiaogen Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 1997 , vol. 45, # 8 p. 3183 - 3189 |
|
~% 
H-PRO-PHE-OH CAS#:13589-02-1 |
| Literature: Freund, Matthias H.; Tsogoeva, Svetlana B. Synlett, 2011 , # 4 p. 503 - 507 |
|
~% 
H-PRO-PHE-OH CAS#:13589-02-1 |
| Literature: Gautschi, Markus; Schmid, Joachim P.; Peppard, Terry L.; Ryan, Thomas P.; Tuorto, Raymond M.; Yang, Xiaogen Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 1997 , vol. 45, # 8 p. 3183 - 3189 |
|
~% 
H-PRO-PHE-OH CAS#:13589-02-1 |
| Literature: Sawayama; Itokawa; Shimada; Doi; Kimura; Nishim ura Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1990 , vol. 38, # 2 p. 529 - 531 |
|
~% 
H-PRO-PHE-OH CAS#:13589-02-1 |
| Literature: Sawayama; Itokawa; Shimada; Doi; Kimura; Nishim ura Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1990 , vol. 38, # 2 p. 529 - 531 |
|
~% 
H-PRO-PHE-OH CAS#:13589-02-1 |
| Literature: Sawayama; Itokawa; Shimada; Doi; Kimura; Nishim ura Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1990 , vol. 38, # 2 p. 529 - 531 |
|
~% 
H-PRO-PHE-OH CAS#:13589-02-1 |
| Literature: Freund, Matthias H.; Tsogoeva, Svetlana B. Synlett, 2011 , # 4 p. 503 - 507 |
|
~% 
H-PRO-PHE-OH CAS#:13589-02-1 |
| Literature: Freund, Matthias H.; Tsogoeva, Svetlana B. Synlett, 2011 , # 4 p. 503 - 507 |
| H-L-Pro-L-Phe-OH |
| N-L-Prolyl-L-phenylalanine |
| PRO-PHE |
| L-Pro-L-Phe-OH |
| pro-phecrystalline |
| Pro-Phe-OH |
| l-pro-l-phe |
| L-Prolyl-L-phenylalanine |
| L-Phenylalanine, L-prolyl- |
| PROLINE-PHENYLALANINE |

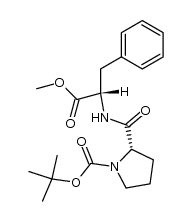
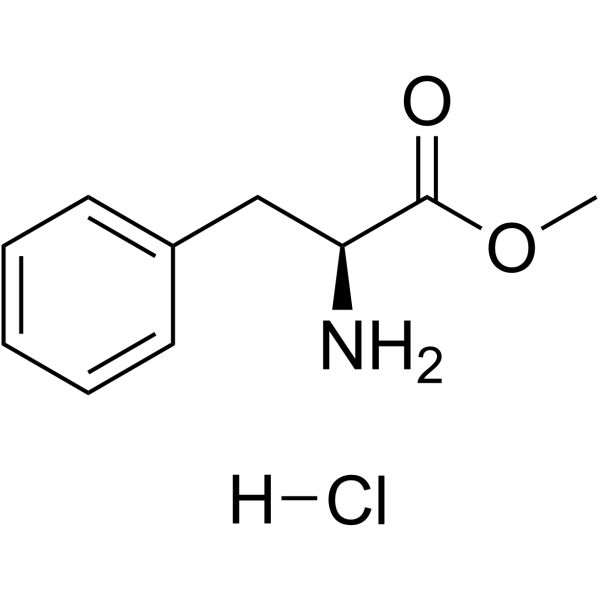

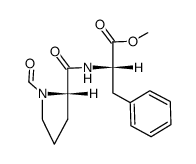

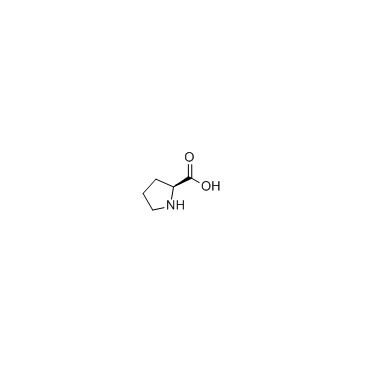

 CAS#:74258-86-9
CAS#:74258-86-9