(R)-Propranolol hydrochloride
Modify Date: 2025-08-24 10:40:19
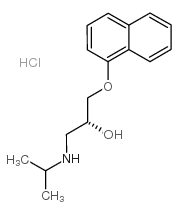
(R)-Propranolol hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | (R)-Propranolol hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13071-11-9 | Molecular Weight | 295.80400 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 434.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H22ClNO2 | Melting Point | 196-198 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 216.8ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of (R)-Propranolol hydrochloride(R)-Propranolol hydrochloride is a less active enantiomer of the β-adrenoceptor antagonist propranolol (HY-B0573). Propranolol is a nonselective β-adrenergic receptor (βAR) antagonist, has high affinity for the β1AR and β2AR with Ki values of 1.8 nM and 0.8 nM, respectively[1]. |
| Name | dexpropranolol hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | (R)-Propranolol hydrochloride is a less active enantiomer of the β-adrenoceptor antagonist propranolol (HY-B0573). Propranolol is a nonselective β-adrenergic receptor (βAR) antagonist, has high affinity for the β1AR and β2AR with Ki values of 1.8 nM and 0.8 nM, respectively[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Both isomers of propranolol are capable of preventing adrenaline-induced cardiac arrhythmias in cats anaesthetized with halothane, but the mean dose of (-)-propranolol is 0.09 mg/kg whereas that of (+)-propranolol is 4.2 mg/kg[1]. Both isomers of propranolol are capable of reversing ventricular tachycardia caused by ouabain in anaesthetized cats and dogs. The dose of (-)-propranolol is significantly smaller than that of (+)-propranolol ((R)-Propranolol) in both species[1]. (R)-Propranolol hydrochloride (10 mg/kg) has no antagonistic activity in rats, the cardiac responses to isoprenaline of rat can be blocked by probably much less than 1/100th of that of the (-) isomer in this preparation[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 434.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 196-198 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C16H22ClNO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 295.80400 |
| Flash Point | 216.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 295.13400 |
| PSA | 41.49000 |
| LogP | 3.77040 |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.48E-08mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | ethanol: 10 mg/mL |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922509090. other amino-alcohol-phenols, amino-acid-phenols and other amino-compounds with oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Effects on feeding rate and biomarker responses of marine mussels experimentally exposed to propranolol and acetaminophen.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 396 , 649-56, (2010) Environmental risk assessments of human pharmaceuticals and other 'emerging contaminants' should integrate both population-relevant endpoints and biomarkers of potential modes of action in a range of ... |
| EINECS 235-961-7 |
| MFCD00066275 |
| (R)-(+)-PROPRANOLOL |
| (R)-Propranolol Hydrochloride |

