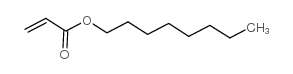
Dioctyl adipate
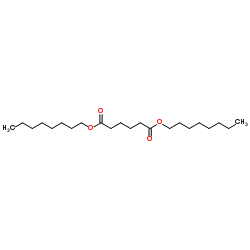
Dioctyl adipate structure
|
Common Name | Dioctyl adipate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 123-79-5 | Molecular Weight | 370.57 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 398.2±10.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H42O4 | Melting Point | -67.8℃ | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 178.6±17.4 °C | |
Use of Dioctyl adipateDioctyl adipate is an organic compound and one of the most commonly used plasticizers for polymerization[1]. |
| Name | dioctyl hexanedioate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dioctyl adipate is an organic compound and one of the most commonly used plasticizers for polymerization[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 398.2±10.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -67.8℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C22H42O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 370.57 |
| Flash Point | 178.6±17.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 370.308319 |
| PSA | 52.60000 |
| LogP | 8.47 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.452 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~93% 
Dioctyl adipate CAS#:123-79-5 |
| Literature: Hansen, Anna Mette; Lindsay, Karl B.; Sudhadevi Antharjanam; Karaffa, Jakob; Daasbjerg, Kim; Flowers II, Robert A.; Skrydstrup, Troels Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006 , vol. 128, # 30 p. 9616 - 9617 |
|
~93% 
Dioctyl adipate CAS#:123-79-5 |
| Literature: Xu, Xiu-Hua; Azuma, Ayaka; Taniguchi, Misaki; Tokunaga, Etsuko; Shibata, Norio RSC Advances, 2013 , vol. 3, # 12 p. 3848 - 3852 |
|
~60% 
Dioctyl adipate CAS#:123-79-5 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 65, # 52 p. 10908 - 10916 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: EP1308208 A1, ; |
| Dicaprylyl adipate |
| Octyl adipate |
| Adimoll DO |
| adipic dioctyl ester |
| Hexanedioic acid, dioctyl ester |
| dicapryl adipate |
| Di-n-octyl adipate |
| Adipinsaeure-dioctylester |
| Dioctyl adipate |
| EINECS 204-652-9 |
| Adipic acid, dioctyl ester |