diisooctyl sebacate
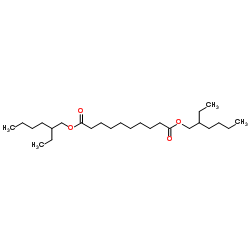
diisooctyl sebacate structure
|
Common Name | diisooctyl sebacate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 122-62-3 | Molecular Weight | 426.673 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 435.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H50O4 | Melting Point | -55 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 189.7±18.2 °C | |
| Name | Bis(2-ethylhexyl) sebacate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 435.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -55 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C26H50O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 426.673 |
| Flash Point | 189.7±18.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 426.370911 |
| PSA | 52.60000 |
| LogP | 9.86 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.454 |
| InChIKey | VJHINFRRDQUWOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCC(CC)COC(=O)CCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(CC)CCCC |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
~96% 
diisooctyl sebacate CAS#:122-62-3 |
| Literature: Sunitha, Sadula; Kanjilal, Sanjit; Reddy, P. Srinivasa; Prasad, Rachapudi B.N. Tetrahedron Letters, 2007 , vol. 48, # 39 p. 6962 - 6965 |
|
~% 
diisooctyl sebacate CAS#:122-62-3 |
| Literature: Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, , vol. 51, p. 673 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 7 | |
| HS Code | 2917131000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2917131000 esters of adipic acid。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Fast synthesis of platinum nanopetals and nanospheres for highly-sensitive non-enzymatic detection of glucose and selective sensing of ions.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 15277, (2015) Novel methods to obtain Pt nanostructured electrodes have raised particular interest due to their high performance in electrochemistry. Several nanostructuration methods proposed in the literature use... |
|
|
Textile-based sampling for potentiometric determination of ions.
Anal. Chim. Acta 877 , 71-9, (2015) Potentiometric sensing utilizing textile-based micro-volume sampling was applied and evaluated for the determination of clinically (Na(+), K(+), Cl(-)) and environmentally (Cd(2+), Pb(2+) and pH) rele... |
|
|
Quantitative determination of fucoidan using polyion-sensitive membrane electrodes.
Anal. Chim. Acta 877 , 1-8, (2015) The use of polyanion and polycation-sensitive membrane electrodes to detect five different preparations of fucoidan is described. Unlike linear polyanionic molecules previously measured with polymer m... |
| di(2-ethylhexyl) sebacate |
| Plexol 201 |
| Decanedioic Acid Di(2-ethylhexyl) Ester |
| Dioctyl sebacate |
| ‘Dioctyl’ sebacate |
| Plasthall DOS |
| Sebacic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester |
| Sebacic acid di(2-ethylhexyl) ester |
| Sebacic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl)ester |
| 2-Ethylhexyl sebacate |
| Bis(2-ethylhexyl) sebacate |
| Decanedioic acid bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester |
| di-2-ethylhexyl sebacate |
| Sebacic Acid Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Ester |
| Sebacic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester (8CI) |
| Bis(2-ethylhexyl)sebacate |
| Sebacic Acid Dioctyl Ester |
| EINECS 204-558-8 |
| Bis(ethylhexyl) sebacate |
| bis(2-ethylhexyl) decanedioate |
| MFCD00009497 |
| UNII:U9LS47Q72Q |
| Decanedioic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester |

 CAS#:1632-16-2
CAS#:1632-16-2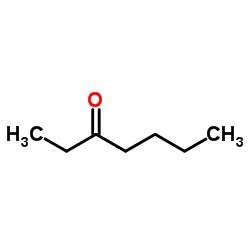 CAS#:106-35-4
CAS#:106-35-4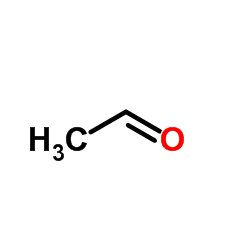 CAS#:75-07-0
CAS#:75-07-0 CAS#:123-38-6
CAS#:123-38-6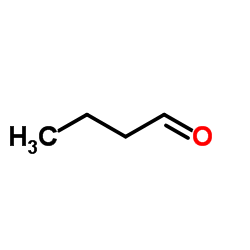 CAS#:123-72-8
CAS#:123-72-8
