Verapamil-d6 hydrochloride
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 07:45:25
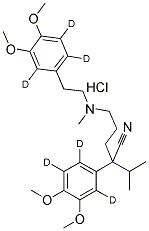
Verapamil-d6 hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Verapamil-d6 hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1185032-80-7 | Molecular Weight | 497.10 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H33D6ClN2O4 | Melting Point | 142°C dec. | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Verapamil-d6 hydrochlorideVerapamil-d6 (CP-16533-1-d6) hydrochloride is the deuterium labled Verapamil (hydrochloride) (HY-A0064). Verapamil hydrochloride ((±)-Verapamil hydrochloride) is a calcium channel blocker and a potent and orally active first-generation P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitor. Verapamil hydrochloride also inhibits CYP3A4. Verapamil hydrochloride has the potential for high blood pressure, heart arrhythmias and angina research[1][2][3]. |
| Name | VERAPAMIL-D6, HYDROCHLORIDE |
|---|
| Description | Verapamil-d6 (CP-16533-1-d6) hydrochloride is the deuterium labled Verapamil (hydrochloride) (HY-A0064). Verapamil hydrochloride ((±)-Verapamil hydrochloride) is a calcium channel blocker and a potent and orally active first-generation P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitor. Verapamil hydrochloride also inhibits CYP3A4. Verapamil hydrochloride has the potential for high blood pressure, heart arrhythmias and angina research[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[1]. Krikler DM. Verapamil in arrhythmia. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;21 Suppl 2:183S-189S. |
| Melting Point | 142°C dec. |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H33D6ClN2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 497.10 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |