(2H5)Benzoic acid
Modify Date: 2025-08-26 12:43:45
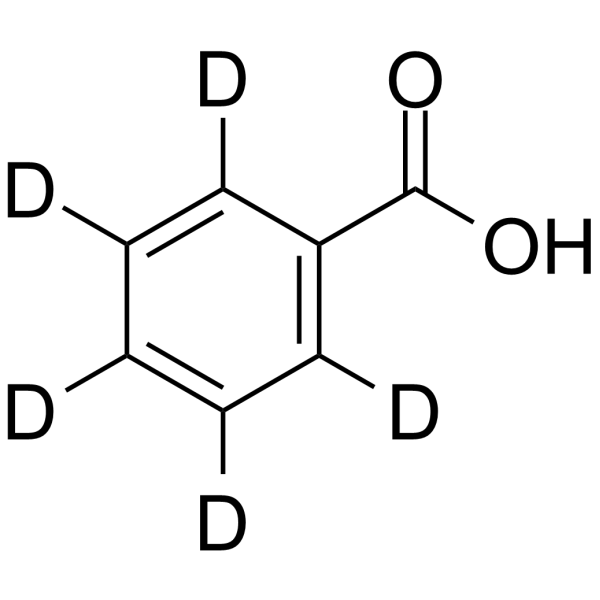
(2H5)Benzoic acid structure
|
Common Name | (2H5)Benzoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1079-02-3 | Molecular Weight | 127.152 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 249.3±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7HD5O2 | Melting Point | 121-125ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 121.1±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of (2H5)Benzoic acidBenzoic acid-d5 is a deuterium substitute for Benzoic acid. Benzoic acid is an aromatic alcohol that occurs naturally in many plants and is a common additive in food, beverages, cosmetics and other products. Benzoic acid can act as a preservative by inhibiting bacteria and fungi[1][2]. |
| Name | benzoic acid-d5 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Benzoic acid-d5 is a deuterium substitute for Benzoic acid. Benzoic acid is an aromatic alcohol that occurs naturally in many plants and is a common additive in food, beverages, cosmetics and other products. Benzoic acid can act as a preservative by inhibiting bacteria and fungi[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. Benzoic acid-d5 can be used for labeling and quantifying the glycopeptides of human serum IgG (hIgG)[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 249.3±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 121-125ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7HD5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 127.152 |
| Flash Point | 121.1±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 127.068161 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 1.89 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.564 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H317-H318-H334-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S26-S36 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
|
Carbon dioxide utilization via carbonate-promoted C-H carboxylation.
Nature 531 , 215-9, (2016) Using carbon dioxide (CO2) as a feedstock for commodity synthesis is an attractive means of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and a possible stepping-stone towards renewable synthetic fuels. A major i... |
| Benzoic-d acid |
| pentadeuterated benzoic acid |
| (H)Benzoic acid |
| Benzoic-d5 acid |
| MFCD00002400 |
| 1,2,3,4,5-pentadeuteriobenzoic acid |
| EINECS 214-089-0 |
| 2,3,4,5,6-pentadeuteriobenzoic acid |
| ring deuterated benzoic acid |
| d5-benzoic acid |
 CAS#:4165-57-5
CAS#:4165-57-5 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9 CAS#:65-85-0
CAS#:65-85-0 CAS#:1603-99-2
CAS#:1603-99-2 CAS#:2037-26-5
CAS#:2037-26-5 CAS#:532-32-1
CAS#:532-32-1 CAS#:1076-43-3
CAS#:1076-43-3 CAS#:84783-81-3
CAS#:84783-81-3 CAS#:43019-90-5
CAS#:43019-90-5 CAS#:18327-98-5
CAS#:18327-98-5 CAS#:14132-51-5
CAS#:14132-51-5 CAS#:17901-93-8
CAS#:17901-93-8 CAS#:71258-22-5
CAS#:71258-22-5 CAS#:71258-23-6
CAS#:71258-23-6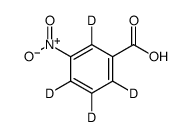 CAS#:78399-78-7
CAS#:78399-78-7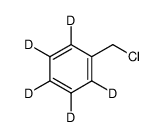 CAS#:68661-11-0
CAS#:68661-11-0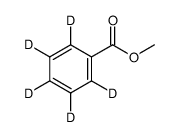 CAS#:68661-19-8
CAS#:68661-19-8