3,4-Dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acid
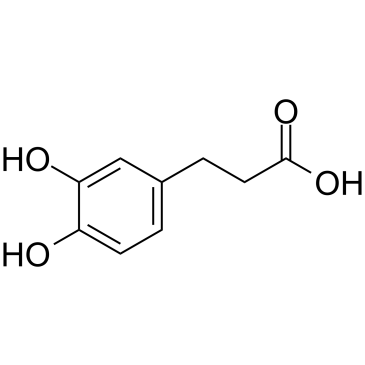
3,4-Dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acid structure
|
Common Name | 3,4-Dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1078-61-1 | Molecular Weight | 182.173 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 417.5±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O4 | Melting Point | 136-139 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 220.4±21.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 3,4-Dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acidDihydrocaffeic acid is a phenolic acid found in Gynura bicolor, reduces phosphorylation of MAPK p38 and prevent UVB-induced skin damage. Antioxidant potential and anti-inflammatory activity[1]. |
| Name | 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dihydrocaffeic acid is a phenolic acid found in Gynura bicolor, reduces phosphorylation of MAPK p38 and prevent UVB-induced skin damage. Antioxidant potential and anti-inflammatory activity[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
p38 MAPK |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 417.5±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 136-139 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 182.173 |
| Flash Point | 220.4±21.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 182.057907 |
| PSA | 77.76000 |
| LogP | 0.50 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.620 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | MW5143500 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
A metabolite profiling approach to identify biomarkers of flavonoid intake in humans.
J. Nucl. Med. 139 , 2309-14, (2009) Flavonoids are phytochemicals that are widespread in the human diet. Despite limitations in their bioavailability, experimental and epidemiological data suggest health benefits of flavonoid consumptio... |
|
|
Poly(N-vinylimidazole/ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) for the purification and isolation of phenolic acids.
Anal. Chim. Acta 885 , 199-206, (2015) In this study we report the novel polymeric resin poly(N-vinyl imidazole/ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) for the purification and isolation of phenolic acids. The monomer to crosslinker ratio and the ... |
|
|
Molecular modifications on carboxylic acid derivatives as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors: Activity and docking studies.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 5219-28, (2009) In the light of known HDAC inhibitors, 33 carboxylic acid derivatives were tested to understand the structural requirements for HDAC inhibition activity. Several modifications were applied to develop ... |
| Dihydrocaffeate |
| 3,4-dihydroxy-hydrocinnamicaci |
| Hydrocaffeate |
| hydrocaffeic acid |
| 3-propionic acid |
| 3,4-Dihydroxy-benzenepropanoic acid |
| 3,4-Dihydroxydihydrocinnamic acid |
| 3-(3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYL)PROPIONIC ACID |
| 3,4-Dihydroxybenzenepropionate |
| 3,4-Dihydroxybenzenepropionic acid |
| dihydrocaffeic acid |
| 3,4-dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acid |
| 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
| 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propionate |
| Benzenepropanoic acid, 3,4-dihydroxy- |
| 3,4-DIHYDROCAFFEIC ACID |
| 3,4-Dihydroxyhydrocinnamate |
| phloretic acid |
| EINECS 214-083-8 |
| 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid,Hydrocaffeic acid |
| Dihydrocafeate |
| MFCD00002776 |
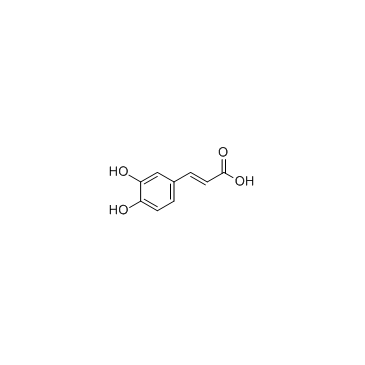 CAS#:331-39-5
CAS#:331-39-5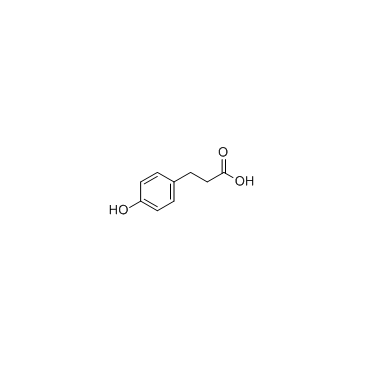 CAS#:501-97-3
CAS#:501-97-3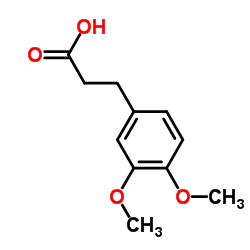 CAS#:2107-70-2
CAS#:2107-70-2 CAS#:2316-26-9
CAS#:2316-26-9 CAS#:1135-23-5
CAS#:1135-23-5 CAS#:132464-92-7
CAS#:132464-92-7![Propanedioic acid,2-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methylene]-, 1,3-diethyl ester Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/019/24331-83-7.png) CAS#:24331-83-7
CAS#:24331-83-7 CAS#:121-33-5
CAS#:121-33-5![3-(2, 3-Dihydrobenzo[b][1, 4]dioXnn-6-yl)propanoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/182/14939-92-5.png) CAS#:14939-92-5
CAS#:14939-92-5 CAS#:120-80-9
CAS#:120-80-9 CAS#:27798-73-8
CAS#:27798-73-8 CAS#:100634-10-4
CAS#:100634-10-4 CAS#:3598-22-9
CAS#:3598-22-9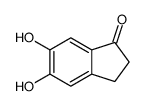 CAS#:124702-80-3
CAS#:124702-80-3 CAS#:79622-99-4
CAS#:79622-99-4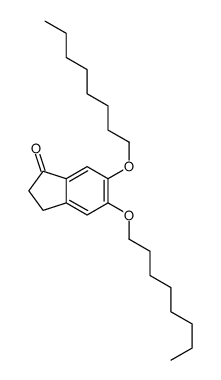 CAS#:92888-48-7
CAS#:92888-48-7
