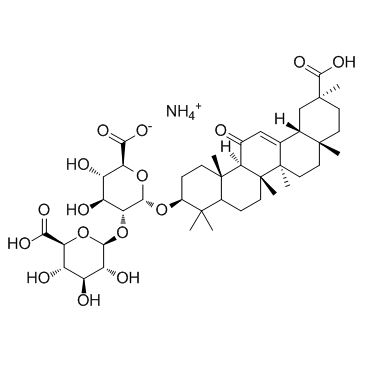
53956-04-0
| Name | Glycyrrhizic acid ammonium salt |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
GLYCAMIL
Ammoniumglycynhizinato glycyrrhizic acid monoammonium salt ammonium glycyrrhizinate MFCD00167400 Glycyrrhizin Monoammonium Salt Hydrate Glycyrrhizic Acid Monoammonium Salt Hydrate (3β)-30-Hydroxy-11,30-dioxoolean-12-en-3-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranuronosyl-α-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid diammoniate GLYCYRRHIZICAMMONIUM Magnasweet ammoniate Monoammonium Glycyrrhizinate Hydrate Glycyrrhizate monoammonium Glycyrrhizin ammonium Glycyrrhiz AMMONIUMGLYCYRRHIZIN Ammonium glycyrrhizate GLYCYRRHIZIC ACID,NH4 ammoniumglycyrrhizate Monoammoniumglycyrrhizinate Glycyrrhizic acid monoammonium salt trihydrate glycyrram EINECS 258-887-7 |
| Description | Monoammonium glycyrrhizinate hydrate has various pharmacological actions such as anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, antigastriculcer, and antihepatitis activities. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | The increase of the lung W/D weight ratios is significantly reduced by high and medium dose of MAG (10 and 30mg/kg) administration. Pretreatment with MAG (10 and 30mg/kg) efficiently reduces the production of TNF-α and IL-1β. MAG (10, 30mg/kg) significantly decreases NF-κB p65 protein expression, compared with LPS. On the contrary, LPS significantly reduces IκB-α protein expression compared with the control group, whereas MAG (10 and 30mg/kg) significantly increased IκB-α expression, compared with the LPS group[1]. Low- and high-dose MAG treatment significantly reduces the AST, ALT, TBIL, and TBA levels at 14 and 21 d time points when compared with that of the RIF and INH group, suggesting the protective effect of MAG on RIF- and INH-induced liver injury. MAG treatment groups elevate the hepatic GSH level at 7, 14, and 21 d time points and markedly reduce the MDA level at 14 and 21 d time points in RIF- and INH-treated rats, suggesting the protective effect of MAG in RIF- and INH induced liver injuries[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] In this study, BALB/c mice (male, 6-8weeks old, and 20-25 g) are used. Mice are randomly divided into five groups: control group, LPS group, and LPS + Monoammonium glycyrrhizinate (MAG: 3, 10, and 30mg/kg) groups. Each group contains eight mice. Mice are anesthetized with intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital (50mg/kg). Before inducing acute lung injury, the mice are given intraperitoneal injection with MAG (3, 10, and 30mg/kg). One hour later, LPS (5mg/kg) is instilled intratracheally to induce acute lung injury. Normal mice are given PBS[1]. Rats[2] Male Wistar rats (180-220 g) are used. Rats are randomly divided into four groups, i.e., control group, RIF and INH group, MAG low-dose group, and MAG high-dose group, each group has 15 rats. Rats in the RIF and INH group receive RIF (60 mg/kg) and INH (60 mg/kg) by gavage administration once daily; rats in MAG groups are pretreated with MAG at the doses of 45 or 90 mg/kg, RIF (60 mg/kg) and INH (60 mg/kg) are given 3 h after MAG administration; rats in the control group are treated with saline. To evaluate the dynamic effect of drugs, rats in each group are sacrificed on 7, 14, and 21 d after drug administration[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.43g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 971.4ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 209ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C42H65NO16 |
| Molecular Weight | 839.96 |
| Flash Point | 288.1ºC |
| PSA | 272.70000 |
| LogP | 0.32860 |
| Index of Refraction | 49 ° (C=1.5, EtOH) |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, practically insoluble in acetone. It dissolves in dilute solutions of acids and of alkali hydroxides. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | LZ6500000 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |